Page 270 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 270
RESISTMTY OF SHALY (CLAYEY) RESERVOIR ROCKS 243
fraction of the shales is at a maximum near the sand bodies and at
a minimum in the shales far from the sands [20].
WATER SATURATION IN SHALY (CLAYEY) RESERVOIR ROCKS
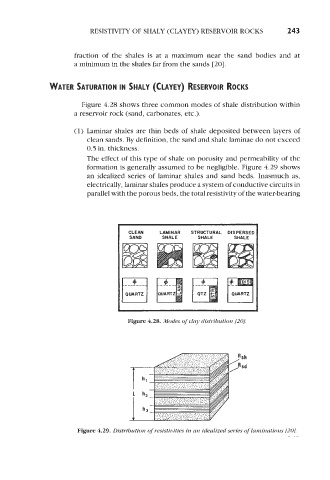
Figure 4.28 shows three common modes of shale distribution within
a reservoir rock (sand, carbonates, etc.).
(1) Laminar shales are thin beds of shale deposited between layers of
clean sands. By definition, the sand and shale laminae do not exceed
0.5 in. thickness.
The effect of this type of shale on porosity and permeability of the
formation is generally assumed to be negligible. Figure 4.29 shows
an idealized series of laminar shales and sand beds. Inasmuch as,
electrically, laminar shales produce a system of conductive circuits in
parallel with the porous beds, the total resistivity of the water-bearing
I CLEAN LAMINAR STRUCTURAL DISPERSED
SAND SHALE SHALE SHALE
Figure 4.28. Modes of clay distribution [ZO].
r
1
1
Figure 4.29. Distribution of resistivities in an idealized series of laminations [20].