Page 29 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 29
4 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
Table 1.1 from analysis of six sandstones. Although the crust appears to be
very heterogeneous with respect to minerals and types of rocks, most of
the rock-forming minerals are composed of silicon and oxygen together
with aluminum and one or more of the other elements listed in Table 1.2.
The chemical compositions and quantitative descriptions of some
minerals are listed in Tables 1.3 and 1.4. Some of the minerals are very
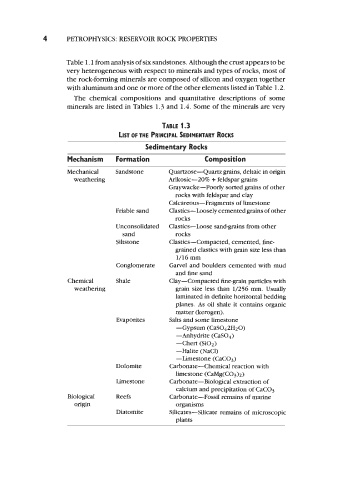
TABLE 1.3
LIST OF THE PRINCIPAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
Sedimentary Rocks
Mechanism Formation Composition
Mechanical Sandstone Quartzose-Quartz grains, deltaic in origin
weathering ArIkosic-20% + feldspar grains
Graywacke-Poorly sorted grains of other
rocks with feldspar and clay
Calcareous-Fragments of limestone
Friable sand Clastics-Loosely cemented grains of other
rocks
Unconsolidated Clastics-Loose sand-grains from other
sand rocks
Siltstone Clastics-Compacted, cemented, fine-
grained clastics with grain size less than
1/16 mm
Conglomerate Garvel and boulders cemented with mud
and fine sand
Chemical Shale Clay-Compacted fine-grain particles with
weathering grain size less than 1/256 111111. Usually
laminated in definite horizontal bedding
planes. As oil shale it contains organic
matter (kerogen).
Evaporites Salts and some limestone
-Gypsum (Cas04 2H2 0)
-Anhydrite (CaSO4)
-Chert (SiOz)
-Halite (NaC1)
-Limestone (CaC03)
Dolomite Carbonate-Chemical reaction with
limestone (CaMg(CO3)z)
Limestone Carbonate-Biological extraction of
calcium and precipitation of CaC03
Biological Reefs Carbonate-Fossil remains of marine
origin organisms
Diatomite Silicates-Silicate remains of microscopic
plants