Page 331 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 331
300 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
TABLE 4.22
BILITH AND TRILITH EQUATIONS
Bilith Equations
At = 189$ 4- 43.5vd01 + 8ovsh + 50Vah (acoustic equation)
rb = 1.1$ + 2.8Nd01 + 2.65vsh + 2.98Vd (density equation)
Trilith Equations
Atc = 189Ifl + 43.51~ + 43.5Vd01 + 55.5vsd + 5OVad (acoustic equation)
rb, = 1.1Ifl + 1.11~ + 2.8Nd01 + 2.65vsd 4- 2.98Vad (density equation)
$NL = 1 .OIn + 1 .OIQ + 0.06Vd01 + 0.03Vsd + O.01Vah (neutron equation)
At = acoustic log input data
Q, = density log input data
Atc = acoustic log data corrected for shale
Q,~ = density log data corrected for shale
$NL = neutron log (limestone mode) data corrected for shale
$ = porosity
If1 = primary porosity index
IQ = secondary porosity index
VdOi, Vsh, Vd, Vsd = percentages of dolomite, shale, anhydrite, and sand,
respectively
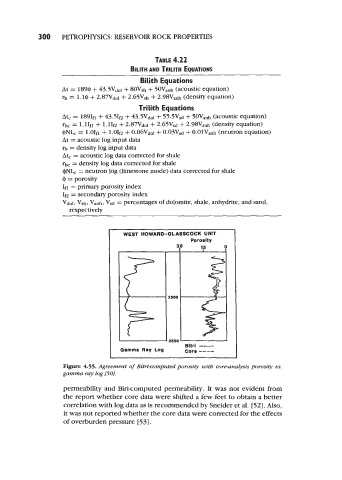
WEST HOWARD-GLASSCOCK UNIT
Porosity
30 15 0
2500
. 2550 Bltrl -
Gamma Ray Log Cor. ----
Figure 4.55. Agreement of Bitri-computed porosity with core-analysis porosity us.
gamma ray log [50].
permeability and Biri-computed permeability. It was not evident from
the report whether core data were shifted a few feet to obtain a better
correlation with log data as is recommended by Sneider et al. [52]. Also,
it was not reported whether the core data were corrected for the effects
of overburden pressure [53].