Page 409 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 409
EVALUATION OF WETTABILITY 377
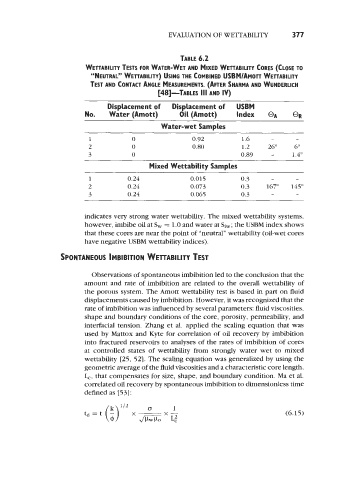
TABLE 6.2
WETTABlLlTY TESTS FOR WATER-WET AND MIXED WETTABlLlTY CORES (CLOSE TO
“NEUTRAL” WETTABILIN) USING THE COMBINED USBM~AMOTT WETTABlLlN
TEST AND CONTACT ANGLE MEASUREMENTS. (AFTER SHARMA AND WUNDERLICH
[48]-TABLES 111 AND Iv)
Displacement of Displacement of USBM
No. Water (Amott) Oil (Amott) Index @A OR
Water-wet Samples
1 0 0.92 1.6 - -
2 0 0.80 1.2 26” 6”
3 0 0.89 - 1.4”
Mixed Wettability Samples
1 0.24 0.015 0.3 - -
2 0.24 0.073 0.3 167” 145”
3 0.24 0.065 0.3 - -
indicates very strong water wettability. The mixed wettability systems,
however, imbibe oil at S, = 1.0 and water at Siw; the USBM index shows
that these cores are near the point of “neutral” wettability (oil-wet cores
have negative USBM wettability indices).
SPONTANEOUS IMBIBITION WETTABILITY TEST
Observations of spontaneous imbibition led to the conclusion that the
amount and rate of imbibition are related to the overall wettability of
the porous system. The Amott wettability test is based in part on fluid
displacements caused by imbibition. However, it was recognized that the
rate of imbibition was influenced by several parameters: fluid viscosities,
shape and boundary conditions of the core, porosity, permeability, and
interfacial tension. Zhang et al. applied the scaling equation that was
used by Mattox and Kyte for correlation of oil recovery by imbibition
into fractured reservoirs to analyses of the rates of imbibition of cores
at controlled states of wettability from strongly water wet to mixed
wettability [25, 521. The scaling equation was generalized by using the
geometric average of the fluid viscosities and a characteristic core length,
L,, that compensates for size, shape, and boundary condition. Ma et al.
correlated oil recovery by spontaneous imbibition to dimensionless time
defined as [ 531 :
(6.15)