Page 503 - Petrophysics
P. 503
MULTIPLE-PERMEABILITY ROCKS 47 1
qt
_I__)
t
i’
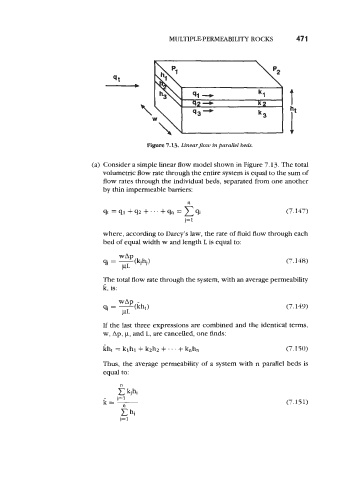
Figure 7.13. LinearJow in parallel beds.
(a) Consider a simple linear flow model shown in Figure 7.13. The total
volumetric flow rate through the entire system is equal to the sum of
flow rates through the individual beds, separated from one another
by thin impermeable barriers:
n
qt = 41 + q2 + . * * + q* = cqi (7.147)
j= 1
where, according to Darcy’s law, the rate of fluid flow through each
bed of equal width w and length L is equal to:
Sj = WAP(kjhj) CLI, (7.148)
The total flow rate through the system, with an average permeability
it. is:
If the last three expressions are combined and the identical terms,
w, Ap, p, and L, are cancelled, one finds:
kht = klhl + k2h2 + . . . + knhn (7.150)
Thus, the average permeability of a system with n parallel beds is
equal to:
(7.15 1)