Page 143 - Physical chemistry understanding our chemical world
P. 143
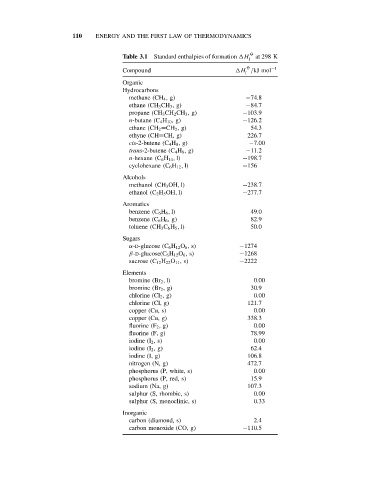
110 ENERGY AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
O
Table 3.1 Standard enthalpies of formation H at 298 K
f
O −1
Compound H /kJ mol
f
Organic
Hydrocarbons
methane (CH 4 ,g) −74.8
ethane (CH 3 CH 3 ,g) −84.7
propane (CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 ,g) −103.9
n-butane (C 4 H 10 ,g) −126.2
ethane (CH 2 =CH 2 ,g) 54.3
ethyne (CH≡CH, g) 226.7
cis-2-butene (C 4 H 8 ,g) −7.00
trans-2-butene (C 4 H 8 ,g) −11.2
n-hexane (C 6 H 14 , l) −198.7
cyclohexane (C 6 H 12 , l) −156
Alcohols
methanol (CH 3 OH, l) −238.7
ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH, l) −277.7
Aromatics
benzene (C 6 H 6 , l) 49.0
benzene (C 6 H 6 ,g) 82.9
toluene (CH 3 C 6 H 5 , l) 50.0
Sugars
α-D-glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ,s) −1274
β-D-glucose(C 6 H 12 O 6 ,s) −1268
sucrose (C 12 H 22 O 11 ,s) −2222
Elements
bromine (Br 2 , l) 0.00
bromine (Br 2 ,g) 30.9
chlorine (Cl 2 ,g) 0.00
chlorine (Cl, g) 121.7
copper (Cu, s) 0.00
copper (Cu, g) 338.3
fluorine (F 2 ,g) 0.00
fluorine (F, g) 78.99
iodine (I 2 ,s) 0.00
iodine (I 2 ,g) 62.4
iodine (I, g) 106.8
nitrogen (N, g) 472.7
phosphorus (P, white, s) 0.00
phosphorus (P, red, s) 15.9
sodium (Na, g) 107.3
sulphur (S, rhombic, s) 0.00
sulphur (S, monoclinic, s) 0.33
Inorganic
carbon (diamond, s) 2.4
carbon monoxide (CO, g) −110.5