Page 178 - Physical Chemistry
P. 178
lev38627_ch05.qxd 3/3/08 9:33 AM Page 159
159
The first integral on the right of (5.34) is evaluated by use of (5.31) and (5.33): Section 5.7
Conventional Entropies and
3
T low C° P,m dT T low aT 3 dT aT 3 T low aT low C° 1T low 2 (5.35) the Third Law
P,m
`
0 T 0 T 3 0 3 3
To evaluate the second integral on the right side of (5.34) and the integral from
T fus to T in (5.29), we can fit polynomials like (5.20) to the measured C° (T) data and
P,m
2
then integrate the resulting expressions for C° /T. Alternatively, we can use graphical
P,m
integration: We plot the measured values of C° (T)/T against T between the relevant
P,m
temperature limits, draw a smooth curve joining the points, and measure the area
under the curve to evaluate the integral. Equivalently, since (C /T) dT C d ln T, we
P
P
can plot C versus ln T and measure the area under the curve.
P
EXAMPLE 5.7 Calculation of S° m,298
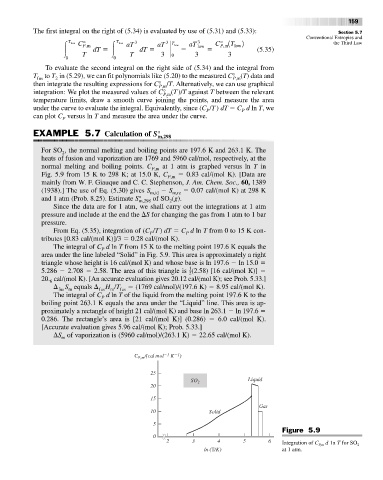
For SO , the normal melting and boiling points are 197.6 K and 263.1 K. The
2
heats of fusion and vaporization are 1769 and 5960 cal/mol, respectively, at the
normal melting and boiling points. C P,m at 1 atm is graphed versus ln T in
Fig. 5.9 from 15 K to 298 K; at 15.0 K, C P,m 0.83 cal/(mol K). [Data are
mainly from W. F. Giauque and C. C. Stephenson, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 60, 1389
(1938).] The use of Eq. (5.30) gives S m,id S m,re 0.07 cal/(mol K) at 298 K
and 1 atm (Prob. 8.25). Estimate S° m,298 of SO (g).
2
Since the data are for 1 atm, we shall carry out the integrations at 1 atm
pressure and include at the end the S for changing the gas from 1 atm to 1 bar
pressure.
From Eq. (5.35), integration of (C /T) dT C d ln T from 0 to 15 K con-
P
P
tributes [0.83 cal/(mol K)]/3 0.28 cal/(mol K).
The integral of C d ln T from 15 K to the melting point 197.6 K equals the
P
area under the line labeled “Solid” in Fig. 5.9. This area is approximately a right
triangle whose height is 16 cal/(mol K) and whose base is ln 197.6 ln 15.0
1
5.286 2.708 2.58. The area of this triangle is (2.58) [16 cal/(mol K)]
2
20. cal/(mol K). [An accurate evaluation gives 20.12 cal/(mol K); see Prob. 5.33.]
6
S equals H /T fus (1769 cal/mol)/(197.6 K) 8.95 cal/(mol K).
m
fus
fus m
The integral of C d ln T of the liquid from the melting point 197.6 K to the
P
boiling point 263.1 K equals the area under the “Liquid” line. This area is ap-
proximately a rectangle of height 21 cal/(mol K) and base ln 263.1 ln 197.6
0.286. The rectangle’s area is [21 cal/(mol K)] (0.286) 6.0 cal/(mol K).
[Accurate evaluation gives 5.96 cal/(mol K); Prob. 5.33.]
S of vaporization is (5960 cal/mol)/(263.1 K) 22.65 cal/(mol K).
m
C P,m /(cal mol K )
1
1
25
SO 2 Liquid
20
15
Gas
10 Solid
5
Figure 5.9
0 ≈
2 3 4 5 6 Integration of C P,m d 1n T for SO 2
ln (T/K) at 1 atm.