Page 277 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 277
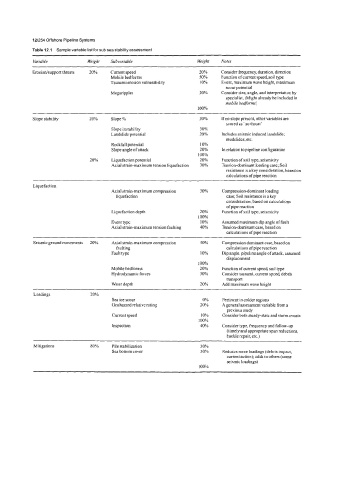
12/254 Offshore Pipeline Systems
Table 12.1 Sample variable list for sub sea stability assessment
Variable Weight Subvariable Weight Notes
Erosionisupport threats 20% Current speed 20% Consider frequency, duration, direction
Mobile bedforms 50% Function of current speed, soil type
Tsunami erosion vulnerability 10% Event, maximum wave height, maximum
scour potential
Megaripples 20% Consider size, angle, and interpretation by
specialist, (Might already be included in
mobile bedforms)
100%
Slope stability 20% Slope% 20% If no slope present, other variables are
scored as ‘no threat’
Slope instability 30%
Landslide potential 20% Includes seismic induced landslide;
mudslides, etc.
Rockfall potential 10%
Slope angle of attack 20% In relation to pipeline configuration
100%
20% Liquefaction potential 20% Function of soil type, seismicity
Axial strain-maximum tension liquefaction 30% Tension-dominant loading case; Soil
resistance is a key consideration, based on
calculations ofpipe reaction
Liquefaction
Axial strain-maximum compression 30% Compression-dominant loading
liquefaction case; Soil resistance is a key
consideration, based on calculations
ofpipe reaction
Liquefaction depth 20% Function of soil type, seismicity
100%
Event type 10% Assumed maximum dip angle of fault
Axial strain-maximum tension faulting 40% Tension-dominant case, based on
calculations ofpipe reaction
Seismic ground movements 20% Axial strain-maximum compression 40% Compression dominant case, based on
faulting calculations of pipe reaction
Fault type 10% Dip angle, pipeline angle ofattack, assumed
displacement
100%
Mobile bedforms 20% Function of current speed, soil type
Hydrodynamic forces 30% Consider tsunami, current speed, debris
transport
Water depth 20% Add maximum wave height
Loadings 20%
Sea ice scour 0% Pertinent in colder regions
Geohazard relative rating 20% A general assessment variable from a
previous study
Current speed 10% Consider both steady-state and storm events
100%
Inspection 40% Consider type, frequency and follow-up
(timely and appropriate span reductions,
buckle repair, etc.)
Mitigations 80% Pile stabilization 30%
Sea bottom cover 30% Reduces some loadings (debris impact,
current action); adds to others (some
seismic loadings)
100%