Page 419 - Pipelines and Risers
P. 419
386 Chapter 20
CURRRFNT WAVE
TO PREVENT
BENDING
TOPTENSIONED 1
CATENARY
RISER RISER
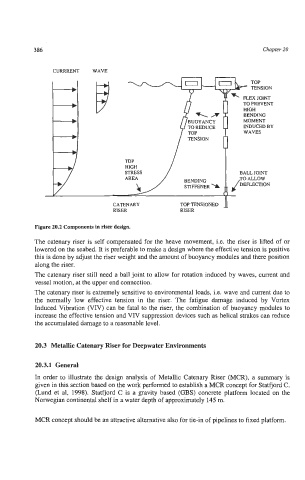
Figure 20.2 Components in riser design.
The catenary riser is self compensated for the heave movement, i.e. the riser is lifted of or
lowered on the seabed. It is preferable to make a design where the effective tension is positive
this is done by adjust the riser weight and the amount of buoyancy modules and there position
along the riser.
The catenary riser still need a ball joint to allow for rotation induced by waves, current and
vessel motion, at the upper end connection.
The catenary riser is extremely sensitive to environmental loads, Le. wave and current due to
the normally low effective tension in the riser. The fatigue damage induced by Vortex
Induced Vibration (VIV) can be fatal to the riser, the combination of buoyancy modules to
increase the effective tension and VIV suppression devices such as helical strakes can reduce
the accumulated damage to a reasonable level.
20.3 Metallic Catenary Riser for Deepwater Environments
20.3.1 General
In order to illustrate the design analysis of Metallic Catenary Riser (MCR), a summary is
given in this section based on the work performed to establish a MCR concept for Statfjord C.
(Lund et al, 1998). Statfjord C is a gravity based (GBS) concrete platform located on the
Norwegian continental shelf in a water depth of approximately 145 m.
MCR concept should be an attractive alternative also for tie-in of pipelines to fixed platform.