Page 311 - Planning and Design of Airports
P. 311
Structural Design of Airport Pavements 269
additional wheels and spacings, were created to distribute increased
gross weights, resulting in equivalent per wheel loads not exceeding
the 350,000 lb maximum.
Equivalent Aircraft Method
Historical airfield pavement design methods recommended by the
FAA beginning in 1975 took into account the varying weights and
landing gear configurations of the fleet of aircraft that may regularly
utilize a given airfield’s pavement. This historical method involved
determining the number of total annual aircraft departures by each
type of aircraft and group them into “equivalent annual departures”
of each aircraft in terms of the landing gear configuration of a given
design aircraft, that is, the aircraft in the fleet mix that requires the
greatest pavement strength. This grouping is based on converting the
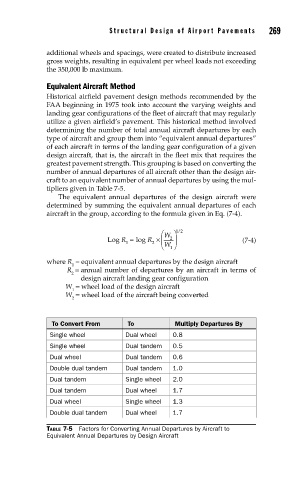
number of annual departures of all aircraft other than the design air-
craft to an equivalent number of annual departures by using the mul-
tipliers given in Table 7-5.
The equivalent annual departures of the design aircraft were
determined by summing the equivalent annual departures of each
aircraft in the group, according to the formula given in Eq. (7-4).
/
⎛ W ⎞ 12
Log R = log R × ⎜ 2 ⎟ (7-4)
1 2
⎝ W 1 ⎠
where R = equivalent annual departures by the design aircraft
1
R = annual number of departures by an aircraft in terms of
2
design aircraft landing gear configuration
W = wheel load of the design aircraft
1
W = wheel load of the aircraft being converted
2
To Convert From To Multiply Departures By
Single wheel Dual wheel 0.8
Single wheel Dual tandem 0.5
Dual wheel Dual tandem 0.6
Double dual tandem Dual tandem 1.0
Dual tandem Single wheel 2.0
Dual tandem Dual wheel 1.7
Dual wheel Single wheel 1.3
Double dual tandem Dual wheel 1.7
TABLE 7-5 Factors for Converting Annual Departures by Aircraft to
Equivalent Annual Departures by Design Aircraft