Page 26 - Plant design and economics for chemical engineers
P. 26
INTRODUCIION 9
N I
I Yield determined by
:: equilibrium between
m I
.E I SO,, 02. a n d SO, D
$J 7 0
\
5 Yield determined I
z A by rate of reaction I
8 2 6 0 between SO, a n d 0, I
I
I
I
I Optimum operation temperature
I
50.
350 400 4 5 0 “0” 5 0 0 5 5 0 6 0 0 6 5 0
Converter temperoture,‘C
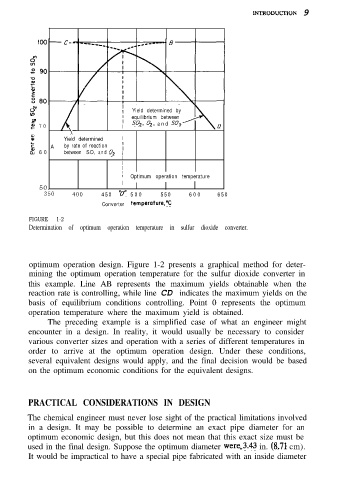
FIGURE 1-2
Determination of optimum operation temperature in sulfur dioxide converter.
optimum operation design. Figure 1-2 presents a graphical method for deter-
mining the optimum operation temperature for the sulfur dioxide converter in
this example. Line AB represents the maximum yields obtainable when the
reaction rate is controlling, while line CD indicates the maximum yields on the
basis of equilibrium conditions controlling. Point 0 represents the optimum
operation temperature where the maximum yield is obtained.
The preceding example is a simplified case of what an engineer might
encounter in a design. In reality, it would usually be necessary to consider
various converter sizes and operation with a series of different temperatures in
order to arrive at the optimum operation design. Under these conditions,
several equivalent designs would apply, and the final decision would be based
on the optimum economic conditions for the equivalent designs.
PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IN DESIGN
The chemical engineer must never lose sight of the practical limitations involved
in a design. It may be possible to determine an exact pipe diameter for an
optimum economic design, but this does not mean that this exact size must be
used in the final design. Suppose the optimum diameter were,3.43 in. (8..71 cm).
It would be impractical to have a special pipe fabricated with an inside diameter