Page 94 - Plant-Based Remediation Processes
P. 94
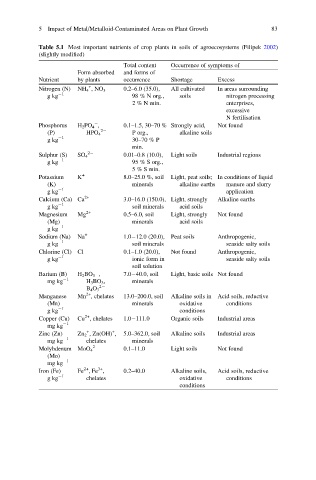
5 Impact of Metal/Metalloid-Contaminated Areas on Plant Growth 83
Table 5.1 Most important nutrients of crop plants in soils of agroecosystems (Filipek 2002)
(slightly modified)
Total content Occurrence of symptoms of
Form absorbed and forms of
Nutrient by plants occurrence Shortage Excess
+
Nitrogen (N) NH 4 ,NO 3 0.2–6.0 (35.0), All cultivated In areas surrounding
gkg 1 98 % N org., soils nitrogen processing
2 % N min. enterprises,
excessive
N fertilisation
Phosphorus H 2 PO 4 , 0.1–1.5, 30–70 % Strongly acid, Not found
(P) HPO 4 2 P org., alkaline soils
gkg 1 30–70 % P
min.
Sulphur (S) SO 4 2 0.01–0.8 (10.0), Light soils Industrial regions
gkg 1 95 % S org.,
5 % S min.
Potassium K + 8.0–25.0 %, soil Light, peat soils; In conditions of liquid
(K) minerals alkaline earths manure and slurry
gkg 1 application
Calcium (Ca) Ca 2+ 3.0–16.0 (150.0), Light, strongly Alkaline earths
gkg 1 soil minerals acid soils
Magnesium Mg 2+ 0.5–6.0, soil Light, strongly Not found
(Mg) minerals acid soils
gkg 1
Sodium (Na) Na + 1.0 12.0 (20.0), Peat soils Anthropogenic,
gkg 1 soil minerals seaside salty soils
Chlorine (Cl) Cl 0.1–1.0 (20.0), Not found Anthropogenic,
gkg 1 ionic form in seaside salty soils
soil solution
Barium (B) H 2 BO 3 , 7.0 40.0, soil Light, basic soils Not found
mg kg 1 H 3 BO 3 , minerals
2
B 4 O 7
2+
Manganese Mn , chelates 13.0–200.0, soil Alkaline soils in Acid soils, reductive
(Mn) minerals oxidative conditions
gkg 1 conditions
2+
Copper (Cu) Cu , chelates 1.0 111.0 Organic soils Industrial areas
mg kg 1
+
+
Zinc (Zn) Zn 2 , Zn(OH) , 5.0–362.0, soil Alkaline soils Industrial areas
mg kg 1 chelates minerals
2 0.1–11.0 Light soils Not found
Molybdenum MoO 4
(Mo)
mg kg 1
2+
3+
Iron (Fe) Fe ,Fe , 0.2–40.0 Alkaline soils, Acid soils, reductive
gkg 1 chelates oxidative conditions
conditions