Page 188 - Plastics Engineering
P. 188
Mechanical Behaviour of Composites 171
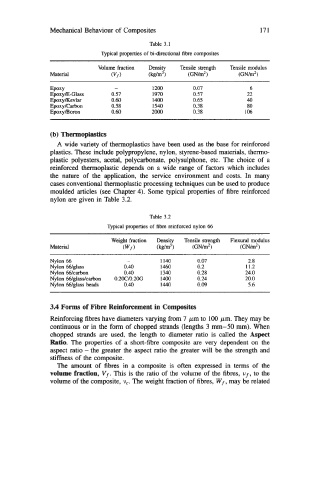
Table 3.1
Qpical properties of bi-directional fibre composites
Volume fraction Density Tensile strength Tensile modulus
1
Material Wf Wm3) (GN/m2) (GN/m2)
EPOXY - 1200 0.07 6
EpoxylE-GlasS 0.57 1970 0.57 22
Epox y/Kevlar 0.60 1400 0.65 40
Epox y/Carbon 0.58 1540 0.38 80
Epox y/Boron 0.60 2000 0.38 106
(b) Thermoplastics
A wide variety of thermoplastics have been used as the base for reinforced
plastics. These include polypropylene, nylon, styrene-based materials, thermo-
plastic polyesters, acetal, polycarbonate, polysulphone, etc. The choice of a
reinforced thermoplastic depends on a wide range of factors which includes
the nature of the application, the service environment and costs. In many
cases conventional thermoplastic processing techniques can be used to produce
moulded articles (see Chapter 4). Some typical properties of fibre reinforced
nylon are given in Table 3.2.
Table 3.2
Typical properties of fibre reinforced nylon 66
Weight fraction Density Tensile strength Flexural modulus
Material (W,) Wm3) (GN/mz) (GN/mz)
Nylon 66 - 1 I40 0.07 2.8
Nylon Wglass 0.40 1460 0.2 11.2
Nylon Wcarbon 0.40 1340 0.28 24.0
Nylon Wglasdcarbon 0.2OC/0.2OG 1400 0.24 20.0
Nylon 66/glass beads 0.40 1440 0.09 5.6
3.4 Forms of Fibre Reinforcement in Composites
Reinforcing fibres have diameters varying from 7 pm to 100 pm. They may be
continuous or in the form of chopped strands (lengths 3 mm-50 mm). When
chopped strands are used, the length to diameter ratio is called the Aspect
Ratio. The properties of a short-fibre composite are very dependent on the
aspect ratio - the greater the aspect ratio the greater will be the strength and
stiffness of the composite.
The amount of fibres in a composite is often expressed in terms of the
volume fraction, Vf. This is the ratio of the volume of the fibres, uf, to the
volume of the composite, u,. The weight fraction of fibres, Wf, may be related