Page 186 - Plastics Engineering
P. 186
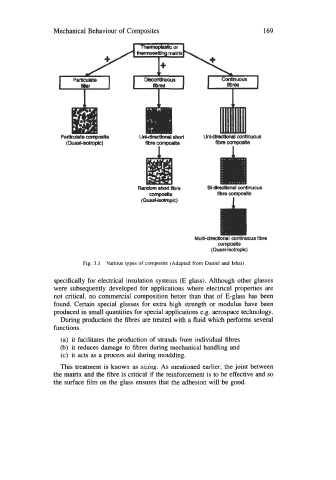
Mechanical Behaviour of Composites 169
Particutate composite UnMirediOnal short UnEdlredknel continuous
(Quasi-isotropic) fibre composite fibre composite
random short fib^ BEdlrectknei continuous
CWnpaQite fibre composite
(QuasCisotropic) I
composite
(Quasi-isotropic)
Fig. 3.1 Various types of composite (Adapted from Daniel and Ishai)
specifically for electrical insulation systems (E glass). Although other glasses
were subsequently developed for applications where electrical properties are
not critical, no commercial composition better than that of E-glass has been
found. Certain special glasses for extra high strength or modulus have been
produced in small quantities for special applications e.g. aerospace technology.
During production the fibres are treated with a fluid which performs several
functions.
(a) it facilitates the production of strands from individual fibres
(b) it reduces damage to fibres during mechanical handling and
(c) it acts as a process aid during moulding.
This treatment is known as sizing. As mentioned earlier, the joint between
the matrix and the fibre is critical if the reinforcement is to be effective and so
the surface film on the glass ensures that the adhesion will be good.