Page 212 - Plastics Engineering
P. 212
Mechanical Behaviour of Composites 195
Directly by matrix manipulation
E, = 1.318 x lod3 cy = -1.509 x yxy = 8.626 x
or by multiplying out the terms
E, = [(s11). (a,) + (512) (ay)] + (516). (txy) E, = 1.318 x
and similarly for the other two strains.
3.8 General Deformation Behaviour of a Single Ply
The previous section has considered the in-plane deformations of a single ply.
In practice, real engineering components are likely to be subjected to this type
of loading plus (or as an alternative) bending deformations. It is convenient
at this stage to consider the flexural loading of a single ply because this will
develop the method of solution for multi-ply laminates.
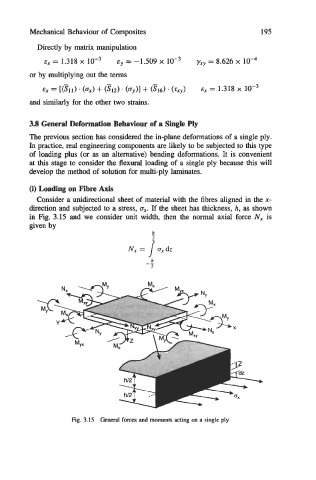
(i) Loading on Fibre Axis
Consider a unidirectional sheet of material with the fibres aligned in the x-
direction and subjected to a stress, u,. If the sheet has thickness, h, as shown
in Fig. 3.15 and we consider unit width, then the normal axial force N, is
given by
!!
2
N, = /ox&
_-
h
2
Fig. 3.15 General forces and moments acting on a single ply