Page 243 - Plastics Engineering
P. 243
226 Mechanical Behaviour of Composites
2.30 x 10-~ -2.24 x 10-~
[ 3.77 x 10-4 5.34 x 10-5 -2.03 x 10-4
2.01 10-~
p = -2.09 x 10-~ 1.49 x 10-~ 9.55 10-~ 1
1.05 x lo3 235.2 -167.1
D = [ 235.2 239.2 -79.2 1
-167.1 -79.2 233.0
2.15 x 10-3 -1.60 10-3 1.64 10-3
-1.601 x 6.65 x -4.04 x
1.64 x 10-~ -4.04 x 10-~ 8.74 10-~
3.14 Analysis of Short Fibre Composites
In order to understand the effect of discontinuous fibres in a polymer matrix
it is important to understand the reinforcing mechanism of fibres. Fibres exert
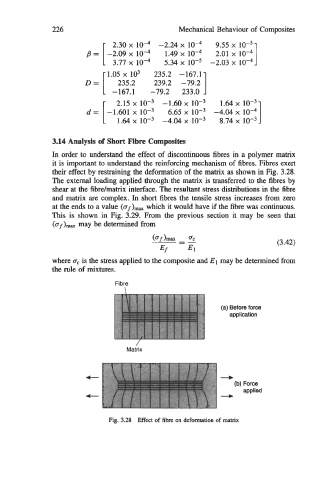
their effect by restraining the deformation of the matrix as shown in Fig, 3.28.
The external loading applied through the matrix is transferred to the fibres by
shear at the fibdmatrix interface. The resultant stress distributions in the fibre
and matrix are complex. In short fibres the tensile stress increases from zero
at the ends to a value (af)- which it would have if the fibre was continuous.
This is shown in Fig. 3.29. From the previous section it may be seen that
(of)- may be determined from
(3.42)
where a, is the stress applied to the composite and E1 may be determined from
the rule of mixtures.
Fibre
\
(a) Before force
application
Matrix
t +
(b) Force
t + applied
Fig. 3.28 Effect of fibre on defonnation of matrix