Page 42 - Plastics Engineering
P. 42
General Properties of Plastics 25
Table 1.6
Balance between stiffness and ductility in thermoplastics
Effect on
Modulus Ductility
Reduced temperature increase decrease
Increased straining rate increase decrease
Multiaxial stress field increase decrease
Incorporation of plasticizer decrease increase
Incorporation of rubbery phase decrease increase
Incorporation of glass fibres increase decrease
Incorporation of particulate filler increase decrease
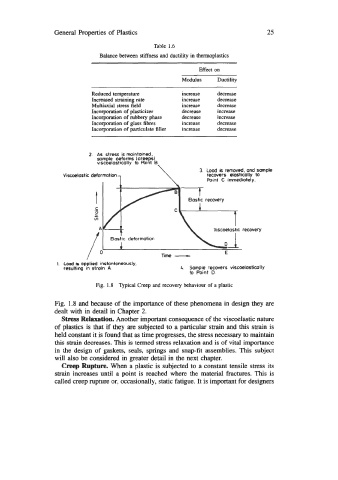
2. As stress is maintained,
sample deforms Icreeps)
viscoelostically to Point B,
3. Load is removed, and sample
Viscoelastic deformation recovers elastically to
Paint C immediately.
Elastic recowry
t
Viscoelastic recovery
1
Time -
1. Load is opplied instantaneously,
resulting in strain A 4. Sample recovers viscoelastically
to Point D
Fig. 1.8 npical Creep and recovery behaviour of a plastic
Fig. 1.8 and because of the importance of these phenomena in design they are
dealt with in detail in Chapter 2.
Stress Relaxation. Another important consequence of the viscoelastic nature
of plastics is that if they are subjected to a particular strain and this strain is
held constant it is found that as time progresses, the stress necessary to maintain
this strain decreases. This is termed stress relaxation and is of vital importance
in the design of gaskets, seals, springs and snap-fit assemblies. This subject
will also be considered in greater detail in the next chapter.
Creep Rupture. When a plastic is subjected to a constant tensile stress its
strain increases until a point is reached where the material fractures. This is
called creep rupture or, occasionally, static fatigue. It is important for designers