Page 165 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 165
Polymer-based nanocomposites 139
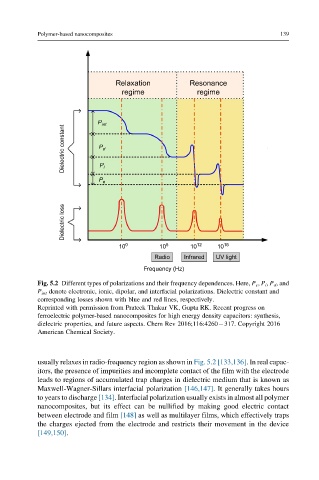
Relaxation Resonance
regime regime
P int
Dielectric constant P d
P P e i
Dielectric loss
10 0 10 6 10 12 10 16
Radio Infrared UV light
Frequency (Hz)
Fig. 5.2 Different types of polarizations and their frequency dependences. Here, P e , P i , P d , and
P int denote electronic, ionic, dipolar, and interfacial polarizations. Dielectric constant and
corresponding losses shown with blue and red lines, respectively.
Reprinted with permission from Prateek Thakur VK, Gupta RK. Recent progress on
ferroelectric polymer-based nanocomposites for high energy density capacitors: synthesis,
dielectric properties, and future aspects. Chem Rev 2016;116:4260 317. Copyright 2016
American Chemical Society.
usually relaxes in radio-frequency region as shown in Fig. 5.2 [133,136]. In real capac-
itors, the presence of impurities and incomplete contact of the film with the electrode
leads to regions of accumulated trap charges in dielectric medium that is known as
Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars interfacial polarization [146,147]. It generally takes hours
to years to discharge [134]. Interfacial polarization usually exists in almost all polymer
nanocomposites, but its effect can be nullified by making good electric contact
between electrode and film [148] as well as multilayer films, which effectively traps
the charges ejected from the electrode and restricts their movement in the device
[149,150].