Page 602 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 602
Nanofibrous composite air filters 555
to describe the overall performance of filter media. It is calculated by the following
equation [5]:
½ ln 1 ηÞ
ð
QF ¼
ΔP
where η indicates the filtration efficiency (the ratio of the number of particles at down-
stream and upstream of the filter sample) and ΔP is the pressure drop (Pa). Darcy’s
law and single fiber theory are generally used to calculate theoretically the pressure
drop and the filtration efficiency, respectively [6].
Chattopadhyay et al. [7] studied the aerosol filtration performance of electrospun
cellulose acetate fibers with different average diameters. The filtration performance of
nanofibrous webs was compared with both glass fiber filters and cellulose acetate
microfiber filters widely used in industry. The QF of electrospun fibers was found
to be slightly higher than glass fiber filter even though thickness of electrospun fiber
is much lower than glass fiber filter. Nanofibrous webs provided higher QF at signi-
ficantly lower basis weight, which is one of the basic advantages of such composite
structures [7].
20.2.2 Fiber alignment
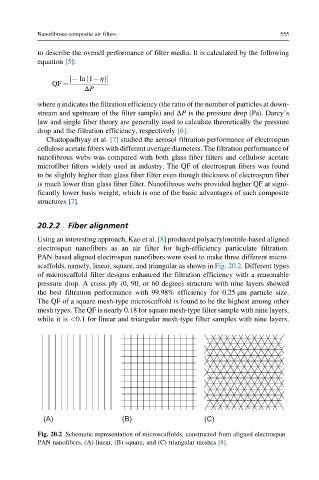
Using an interesting approach, Kao et al. [8] produced polyacrylonitrile-based aligned
electrospun nanofibers as an air filter for high-efficiency particulate filtration.
PAN-based aligned electrospun nanofibers were used to make three different micro-
scaffolds, namely, linear, square, and triangular as shown in Fig. 20.2. Different types
of microscaffold filter designs enhanced the filtration efficiency with a reasonable
pressure drop. A cross ply (0, 90, or 60 degree) structure with nine layers showed
the best filtration performance with 99.98% efficiency for 0.25 μm particle size.
The QF of a square mesh-type microscaffold is found to be the highest among other
mesh types. The QF is nearly 0.18 for square mesh-type filter sample with nine layers,
while it is <0.1 for linear and triangular mesh-type filter samples with nine layers.
(A) (B) (C)
Fig. 20.2 Schematic representation of microscaffolds, constructed from aligned electrospun
PAN nanofibers, (A) linear, (B) square, and (C) triangular meshes [8].