Page 654 - Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
P. 654
[50]
[52]
[44]
[53]
[48]
[49]
[45]
[51]
[54]
[47]
[56]
[55]
900–1450,
g 1
μmol
and
1650–1700,
800–1050,
600–1350
263.157
1149.4
52
17.36
58.82
16.73
167.5
18.1
671
192
56,
–
Pb(II),
Cd(II)
(III),
(II)
(V)
Hg(II),
Cr(VI)
Cr(VI)
Cr(VI)
Cr(VI)
Cr(VI)
Cr(VI)
Cu(II),
Hg(II)
Hg(II)
Ni(II)
Mn
As
As
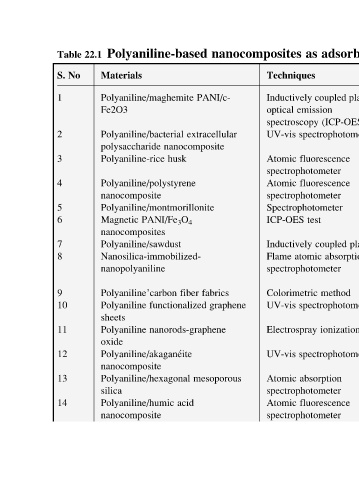
adsorbents 604 ions metal of removal the for Reference mg/g (qe) Capacity ions Metals [43] 106.8 195.7, (II) Cu Cr(VI), plasma- (ICP-OES) [46] 68.40 Cr(VI) spectrophotometer Polymer-based Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications
plasma
spectrophotometer
spectrophotometer
absorption
ionization
method
as Techniques coupled Inductively emission spectroscopy fluorescence spectrophotometer fluorescence spectrophotometer Spectrophotometer test ICP-OES coupled Inductively atomic spectrophotometer Colorimetric Electrospray absorption spectrophotometer fluorescence spectrophotometer
nanocomposites PANI/c- optical UV-vis extracellular Atomic Atomic Flame fabrics UV-vis graphene UV-vis Atomic mesoporous Atomic
Polyaniline-based Polyaniline/maghemite Polyaniline/bacterial nanocomposite polysaccharide husk Polyaniline-rice Polyaniline/polystyrene nanocomposite Polyaniline/montmorillonite PANI/Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites Polyaniline/sawdust Nanosilica-immobilized- nanopolyaniline fiber Polyaniline’carbon functionalized nanorods-gra
22.1 Materials Fe2O3 Magnetic Polyaniline sheets Polyaniline oxide silica
Table No S. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14