Page 124 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 124
99
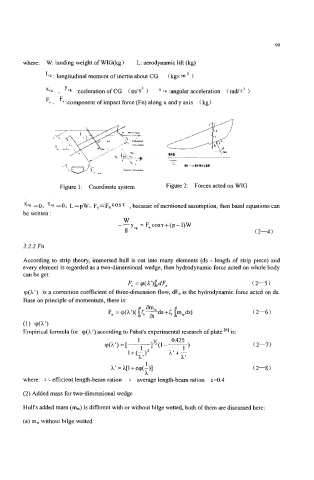
where: W landing weight of WIG(kg) L: aerodynamic lift (kg)
: longitudinal moment of inertia about CG (kgx m 1
xcg . ycg :cceleration of CG (dS2 1 c* :angular acceleration (rads* 1
Fx . Fy :component of impact force (Fn) along x and y axis (kg )
Figure 1 : Coordinate system Figure 2: Forces acted on WIG
xcg = 0, ' = 0, L = pW , F,= F, COS 7 , because of mentioned assumption, then basal equations can
cg
be written :
3.2.2 Fn
According to strip theory, immersed hull is cut into many elements (ds - length of strip piece) and
every element is regarded as a two-dimensional wedge, then hydrodynamic force acted on whole body
can be get:
F, = p(n')$dF, ( 2-5 1
cp(h') is a correction coefficient of three-dimension flow, dF, is the hydrodynamic force acted on ds.
Base on principle of momentum, there is:
F, = q(h')( [i3s+< [m,ds) ( 2-6 )
(1) dh')
Empirical formula for cp(h') according to Pabst's experimental research of plate is:
1
h' = h[l + d-)] ( 2-8 )
h
where: *- efficient length-beam ration - average length-beam ration c=0.4
(2) Added mass for two-dimensional wedge
Hull's added mass (m,) is different with or without bilge wetted, both of them are discussed here:
(a) m, without bilge wetted