Page 218 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 218
193
- 2
CI
- I i3u'
f
- 90 188 - 90
I88
I88
90
VO
z 3 z 0 30
-90 -90 I
-90
-180 -180 -180
2 4 w (rndh] 4 6 w [rad/,] 8
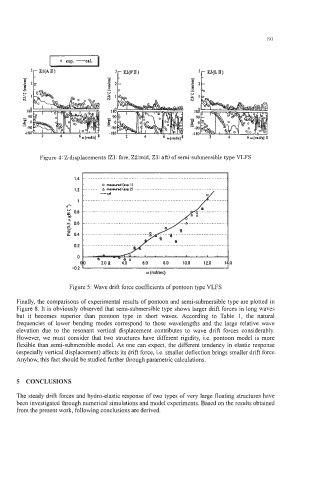
Figure 4: Z-displacements (Z1: fore, ZZ:mid, 23: aft) of semi-submersible type VLFS
I
i
1.4 t ....................................................................................... 1
0 nw.d (em 1)
12 .......... A ms-d(exp2) .........................................................
-4
00 2.0 a 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0
Figure 5: Wave drift force coefficients of pontoon type VLFS
Finally, the comparisons of experimental results of pontoon and semi-submersible type are plotted in
Figure 8. It is obviously observed that semi-submersible type shows larger drift forces in long waves
but it becomes superior than pontoon type in short waves. According to Table 1, the natural
frequencies of lower bending modes correspond to those wavelengths and the large relative wave
elevation due to the resonant vertical displacement contributes to wave drift forces considerably.
However, we must consider that two structures have different rigidity, i.e. pontoon model is more
flexible than semi-submersible model. As one can expect, the different tendency in elastic response
(especially vertical displacement) affects its drift force, Le. smaller deflection brings smaller drift force.
Anyhow, this fact should be studied further through parametric calculations.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The steady drift forces and hydro-elastic response of two types of very large floating structures have
been investigated through numerical simulations and model experiments. Based on the results obtained
from the present work, following conclusions are derived.