Page 274 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 274
249
m m
4) model four: M(* ,e), i.e, b, = c(a,r,, (j=1, 2, .... n) or 6, = min{l,x(a,r,, )} (j=1, 2, .... n)
)
,=I ,=I
111
5) Model five: M(*,+)and thus b, = Ea,?, (j=l, 2, .... n)
/ U,”
....... .1Ul”
/u* ........................
\
” \ / ....... :Ll q
?
.I
%TW
kb b*
-2ndleVcl VI) 10 CakwlieS
tbmrehmanv level
Figure 2: Multi-Level Comprehensive Fuzzy Assessment
3 APPLICATION OF THE COMPREHENSIVE FUZZY METHOD IN HAZARD
IDENTIFICATION OF FORMAL SAFETY ASSESSMENT (FSA)
The all of kind of subsystem are as follows:
3.1 Crew Subsystem
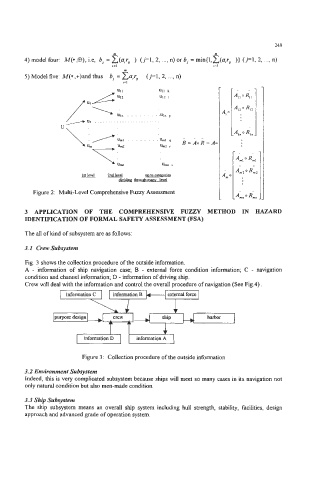
Fig. 3 shows the collection procedure of the outside information.
A - information of ship navigation case; B - external force condition information; C - navigation
condition and channel information; D - information of driving ship.
Crew will deal with the information and control the overall procedure of navigation (See Fig.4) .
I
[i”””””””,”] informationB external force
purpose design
Figure 3: Collection procedure of the outside information
3.2 Environment Subsystem
Indeed, this is very complicated subsystem because ships will meet so many cases in its navigation not
only natural condition but also men-made condition.
3.3 Ship Subsystem
The ship subsystem means an overall ship system including hull strength, stability, facilities, design
approach and advanced grade of operation system.