Page 408 - Practical Design Ships and Floating Structures
P. 408
383
the handling and transport of raw and fabricated materials, prefabrication and fabrication processes:
cutting, forming of plates and sections, welding and assembly of steel plates and sections, construction
of 2D and 3D blocks, assembly of blocks on bertwdock, outfitting and painting operations, tests and
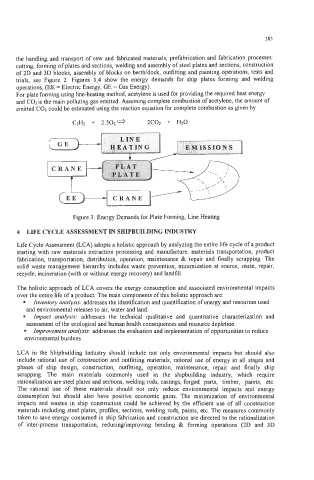
trials, see Figure 2. Figures 3,4 show the energy demands for ship plates forming and welding
operations, (EE = Electric Energy, GE = Gas Energy).
For plate forming using line-heating method, acetylene is used for providing the required heat energy
and COz is the main polluting gas emitted. Assuming complete combustion of acetylene, the amount of
emitted COz could be estimated using the reaction equation for complete combustion as given by:
CzHz + 2.50~~ 2COz + HzO
I
EE CRANE
Figure 3 : Energy Demands for Plate Forming, Line Heating
4 LIFE CYCLE ASSESSMENT IN SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) adopts a holistic approach by analyzing the entire life cycle of a product
starting with raw materials extraction processing and manufacture, materials transportation, product
fabrication, transportation, distribution, operation, maintenance & repair and finally scrapping. The
solid waste management hierarchy includes waste prevention, minimization at source, reuse, repair,
recycle, incineration (with or without energy recovery) and landfill.
.
The holistic approach of LCA covers the energy consumption and associated environmental impacts
over the entire life of a product. The main components of this holistic approach are:
Inventory analysis: addresses the identification and quantification of energy and resources used
and environmental releases to air, water and land.
Impact analysis: addresses the technical qualitative and quantitative characterization and
assessment of the ecological and human health consequences and resource depletion.
Improvement analyszs: addresses the evaluation and implementation of opportunities to reduce
environmental burdens
LCA in the Shipbuilding Industry should include not only environmental impacts but should also
include rational use of construction and outfitting materials, rational use of energy in all stages and
phases of ship design, construction, outfitting, operation, maintenance, repair and finally ship
scrapping. The main materials commonly used in the shipbuilding industry, which require
rationalization are steel plates and sections, welding rods, castings, forged parts, timber, paints, etc.
The rational use of these materials should not only reduce environmental impacts and energy
consumption but should also have positive economic gains. The minimization of environmental
impacts and wastes in ship construction could be achieved by the efficient use of all construction
materials including steel plates, profiles, sections, welding rods, paints, etc. The measures commonly
taken to save energy consumed in ship fabrication and construction are directed to the rationalization
of inter-process transportation, reducinglimproving bending & forming operations (2D and 3D