Page 57 - Practical Well Planning and Drilling Manual
P. 57
Section 1 revised 11/00/bc 1/17/01 2:55 PM Page 33
Precompletion and Completion Design [ ]
1.3.5
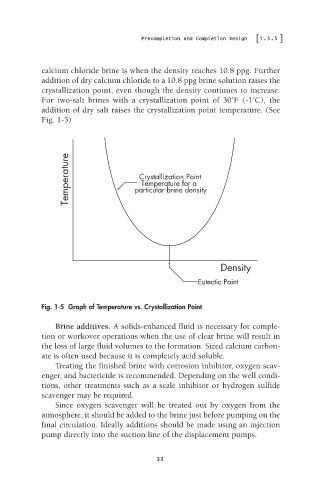
calcium chloride brine is when the density reaches 10.8 ppg. Further
addition of dry calcium chloride to a 10.8 ppg brine solution raises the
crystallization point, even though the density continues to increase.
For two-salt brines with a crystallization point of 30˚F (-1˚C), the
addition of dry salt raises the crystallization point temperature. (See
Fig. 1-5)
Fig. 1-5 Graph of Temperature vs. Crystallization Point
Brine additives. A solids-enhanced fluid is necessary for comple-
tion or workover operations when the use of clear brine will result in
the loss of large fluid volumes to the formation. Sized calcium carbon-
ate is often used because it is completely acid soluble.
Treating the finished brine with corrosion inhibitor, oxygen scav-
enger, and bactericide is recommended. Depending on the well condi-
tions, other treatments such as a scale inhibitor or hydrogen sulfide
scavenger may be required.
Since oxygen scavenger will be treated out by oxygen from the
atmosphere, it should be added to the brine just before pumping on the
final circulation. Ideally additions should be made using an injection
pump directly into the suction line of the displacement pumps.
33