Page 90 - Practical Well Planning and Drilling Manual
P. 90
Section 1 revised 11/00/bc 1/17/01 2:56 PM Page 66
[ ] Well Design
1.4.10
For steel (SG 7.87), the buoyancy factor when immersed in mud
can be simplified to:
BF =- (0 2936. r ) =-1 (0 0153. ppg )
1
where r is the mud gradient in psi/ft or ppg is the mud weight in
pounds per gallon.
If aluminum were in use (e.g., aluminum drillpipe) then the buoy-
ancy factor can be calculated from the SG for Al, which is 2.75.
Buoyancy factor can be used for calculating the immersed weight
of a drillstring (which fills as it is run in) or of casing that is filled
with mud of the same density as the fluid outside.
Using buoyancy factor to calculate axial stress in a string of tubing
only yields an accurate result at the top of the string.
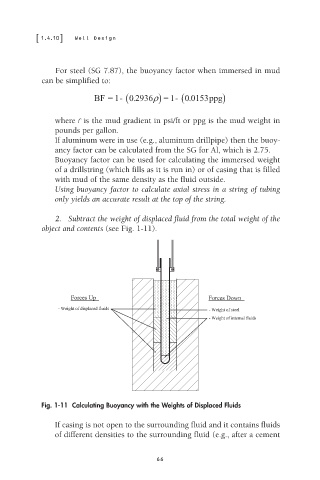
2. Subtract the weight of displaced fluid from the total weight of the
object and contents (see Fig. 1-11).
Forces Up Forces Down
- Weight of displaced fluids - Weight of steel
- Weight of internal fluids
Fig. 1-11 Calculating Buoyancy with the Weights of Displaced Fluids
If casing is not open to the surrounding fluid and it contains fluids
of different densities to the surrounding fluid (e.g., after a cement
66