Page 131 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 131
Gas flooding 121
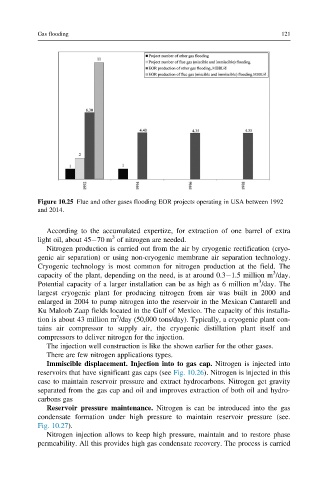
Figure 10.25 Flue and other gases flooding EOR projects operating in USA between 1992
and 2014.
According to the accumulated expertize, for extraction of one barrel of extra
3
light oil, about 45 70 m of nitrogen are needed.
Nitrogen production is carried out from the air by cryogenic rectification (cryo-
genic air separation) or using non-cryogenic membrane air separation technology.
Cryogenic technology is most common for nitrogen production at the field. The
3
capacity of the plant, depending on the need, is at around 0.3 1.5 million m /day.
3
Potential capacity of a larger installation can be as high as 6 million m /day. The
largest cryogenic plant for producing nitrogen from air was built in 2000 and
enlarged in 2004 to pump nitrogen into the reservoir in the Mexican Cantarell and
Ku Maloob Zaap fields located in the Gulf of Mexico. The capacity of this installa-
3
tion is about 43 million m /day (50,000 tons/day). Typically, a cryogenic plant con-
tains air compressor to supply air, the cryogenic distillation plant itself and
compressors to deliver nitrogen for the injection.
The injection well construction is like the shown earlier for the other gases.
There are few nitrogen applications types.
Immiscible displacement. Injection into to gas cap. Nitrogen is injected into
reservoirs that have significant gas caps (see Fig. 10.26). Nitrogen is injected in this
case to maintain reservoir pressure and extract hydrocarbons. Nitrogen get gravity
separated from the gas cap and oil and improves extraction of both oil and hydro-
carbons gas
Reservoir pressure maintenance. Nitrogen is can be introduced into the gas
condensate formation under high pressure to maintain reservoir pressure (see.
Fig. 10.27).
Nitrogen injection allows to keep high pressure, maintain and to restore phase
permeability. All this provides high gas condensate recovery. The process is carried