Page 22 - Primer on Enhanced Oil Recovery
P. 22
Hydrocarbon and oil reserves classification 13
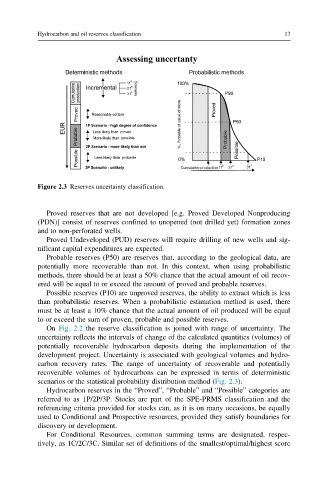
Figure 2.3 Reserves uncertainty classification.
Proved reserves that are not developed [e.g. Proved Developed Nonproducing
(PDN)] consist of reserves confined to unopened (not drilled yet) formation zones
and to non-perforated wells.
Proved Undeveloped (PUD) reserves will require drilling of new wells and sig-
nificant capital expenditures are expected.
Probable reserves (P50) are reserves that, according to the geological data, are
potentially more recoverable than not. In this context, when using probabilistic
methods, there should be at least a 50% chance that the actual amount of oil recov-
ered will be equal to or exceed the amount of proved and probable reserves.
Possible reserves (P10) are unproved reserves, the ability to extract which is less
than probabilistic reserves. When a probabilistic estimation method is used, there
must be at least a 10% chance that the actual amount of oil produced will be equal
to or exceed the sum of proven, probable and possible reserves.
On Fig. 2.2 the reserve classification is joined with range of uncertainty. The
uncertainty reflects the intervals of change of the calculated quantities (volumes) of
potentially recoverable hydrocarbon deposits during the implementation of the
development project. Uncertainty is associated with geological volumes and hydro-
carbon recovery rates. The range of uncertainty of recoverable and potentially
recoverable volumes of hydrocarbons can be expressed in terms of deterministic
scenarios or the statistical probability distribution method (Fig. 2.3).
Hydrocarbon reserves in the “Proved”, “Probable” and “Possible” categories are
referred to as 1P/2P/3P. Stocks are part of the SPE-PRMS classification and the
referencing criteria provided for stocks can, as it is on many occasions, be equally
used to Conditional and Prospective resources, provided they satisfy boundaries for
discovery or development.
For Conditional Resources, common summing terms are designated, respec-
tively, as 1C/2C/3C. Similar set of definitions of the smallest/optimal/highest score