Page 119 - Principles and Applications of NanoMEMS Physics
P. 119
3. NANOMEMS PHYSICS: Quantum Wave Phenomena 107
Carbon Nanotube
Carbon Nanotube
Axis
Axis
unit
unit
(a)
Carbon Nanotube
Carbon Nanotube
Axis
Axis
unit
unit
(b)
Carbon Nanotube
Carbon Nanotube
Axis
Axis
Chiral Vector
Chiral Vector
θ θ
(c)
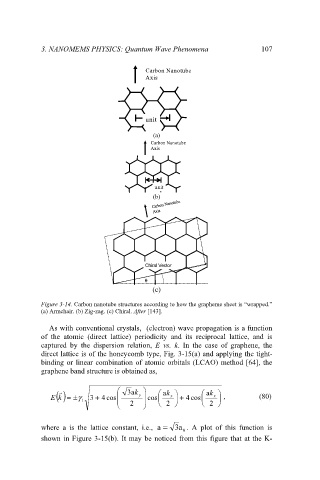
Figure 3-14. Carbon nanotube structures according to how the grapheme sheet is “wrapped.”
(a) Armchair. (b) Zig-zag. (c) Chiral. After [143].
As with conventional crystals, (electron) wave propagation is a function
of the atomic (direct lattice) periodicity and its reciprocal lattice, and is
captured by the dispersion relation, E vs. k. In the case of graphene, the
direct lattice is of the honeycomb type, Fig. 3-15(a) and applying the tight-
binding or linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method [64], the
graphene band structure is obtained as,
G § 3 ak · § ak · § ak ·
E () ±= γ 3 + cos ¨ y ¸ cos ¨ x ¸ + cos4 ¨ x ¸ , (80)
4
k
1 ¨ 2 ¸ © 2 © 2
© ¹ ¹ ¹
where a is the lattice constant, i.e., a = a 3 0 . A plot of this function is
shown in Figure 3-15(b). It may be noticed from this figure that at the K-