Page 155 - Principles and Applications of NanoMEMS Physics
P. 155
3. NANOMEMS PHYSICS: Quantum Wave Phenomena 143
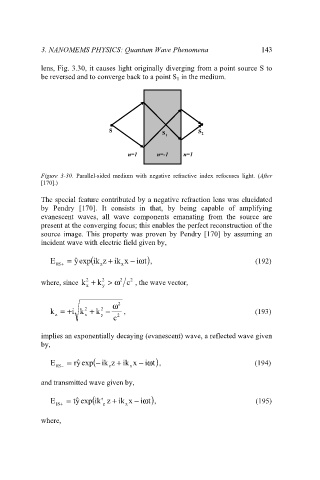
lens, Fig. 3.30, it causes light originally diverging from a point source S to
be reversed and to converge back to a point S 1 in the medium.
S S S S
S S 1 1 2 2
n=1 n=-1 n=1
n=-1
n=1
n=1
Figure 3-30. Parallel-sided medium with negative refractive index refocuses light. (After
[170].)
The special feature contributed by a negative refraction lens was elucidated
by Pendry [170]. It consists in that, by being capable of amplifying
evanescent waves, all wave components emanating from the source are
present at the converging focus; this enables the perfect reconstruction of the
source image. This property was proven by Pendry [170] by assuming an
incident wave with electric field given by,
E = y ˆ exp (ik z + ik x − iω ) t , (192)
0 S+ z x
where, since k + k > ω 2 c , the wave vector,
2
2
2
x y
ω 2
k = i + k + k − , (193)
2
2
z x y 2
c
implies an exponentially decaying (evanescent) wave, a reflected wave given
by,
E = y ˆ r exp ( ik− z + ik x − iω ) t , (194)
0 S− z x
and transmitted wave given by,
E = y ˆ t exp ( 'ik z + ik x − iω ) t , (195)
1 S+ z x
where,