Page 245 - Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation 2E
P. 245
230 Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation
and reservoir engineering features have been added to WINB4D, including the
ability to perform material balance studies with a tank model, the representation
of horizontal or deviated wells, and the calculation of important reservoir
geophysical information.
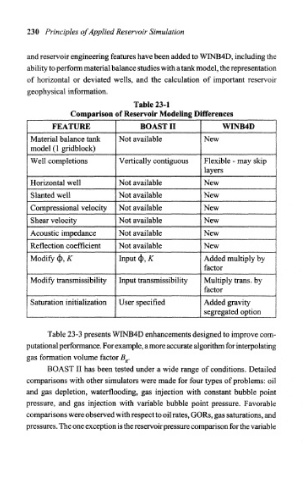
Table 23-1
Comparison of Reservoir Modeling Differences
FEATURE BOAST II WINB4D
Material balance tank Not available New
model (1 gridblock)
Well completions Vertically contiguous Flexible - may skip
layers
Horizontal well Not available New
Slanted well Not available New
Compressional velocity Not available New
Shear velocity Not available New
Acoustic impedance Not available New
Reflection coefficient Not available New
Modify (|>, K Input <J>, K Added multiply by
factor
Modify transmissibility Input transmissibility Multiply trans, by
factor
Saturation initialization User specified Added gravity
segregated option
Table 23-3 presents WINB4D enhancements designed to improve com-
putational performance. For example, a more accurate algorithm for interpolating
gas formation volume factor B g.
BOAST II has been tested under a wide range of conditions. Detailed
comparisons with other simulators were made for four types of problems: oil
and gas depletion, waterflooding, gas injection with constant bubble point
pressure, and gas injection with variable bubble point pressure. Favorable
comparisons were observed with respect to oil rates, GORs, gas saturations, and
pressures. The one exception is the reservoir pressure comparison for the variable