Page 45 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 45
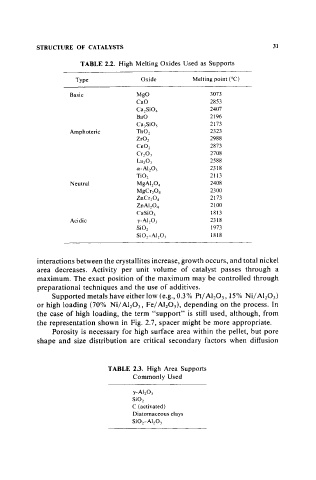
STRUcrURE OF CATALYSTS 31
TABLE 2.2. High Melting Oxides Used as Supports
Type Oxide Melting point (DC)
Basic MgO 3073
CaO 2853
CazSi0 4 2407
BaO 2196
CaJSiOs 2173
Amphoteric ThOz 2323
ZrOz 2988
CeOz 2873
Cr20J 2708
La203 2588
a-AI2 OJ 2318
Ti02 2113
Neutral MgAI2 04 2408
2300
MgCr2 0 4
ZnCr Z0 4 2173
ZnAlz0 4 2100
CaSiOJ 1813
Acidic y-AlzOJ 2318
SiOz 1973
Si0z-AI203 1818
interactions between the crystallites increase, growth occurs, and total nickel
area decreases. Activity per unit volume of catalyst passes through a
maximum. The exact position of the maximum may be controlled through
preparational techniques and the use of additives.
Supported metals have either low (e.g., 0.3% Pt/ A1 20 3 , 15% Nil A1 20 3 )
or high loading (70% Nil A1 20 3 , Fe/ AI 20 3 ), depending on the process. In
the case of high loading, the term "support" is still used, although, from
the representation shown in Fig. 2.7, spacer might be more appropriate.
Porosity is necessary for high surface area within the pellet, but pore
shape and size distribution are critical secondary factors when diffusion
TABLE 2.3. High Area Supports
Commonly Used
y-Al z0 3
SiOz
C (activated)
Diatomaceous clays
SiOr AI 20 J