Page 64 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 64
CATALYTIC MATERIALS 51
IA IIA
LI Be
Na Mg
K Ce
"s" METALS
Rb Sr
Cs Ba
Fr Ra
IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB VIII IB
Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu
TRANSITION
"d" METALS V Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag
La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir PI Au
RARE EARTH "f" METALS
I Ce I Pr I Nd I Pm I Sm I Eu I Gd I Tb I Oy I Ho I Er I Tm I Vb Lu
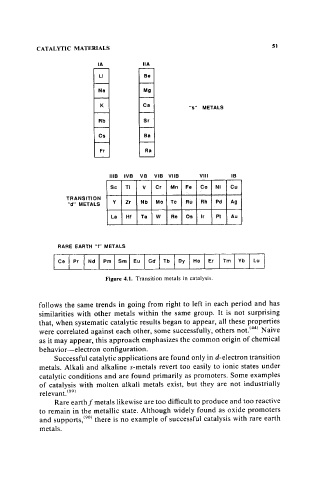
Figure 4.1. Transition metals in catalysis.
follows the same trends in going from right to left in each period and has
similarities with other metals within the same group. It is not surprising
that, when systematic catalytic results began to appear, all these properties
were correlated against each other, some successfully, others not.(44) Naive
as it may appear, this approach emphasizes the common origin of chemical
behavior-electron configuration.
Successful catalytic applications are found only in d-electron transition
metals. Alkali and alkaline s-metals revert too easily to ionic states under
catalytic conditions and are found primarily as promoters. Some examples
of catalysis with molten alkali metals exist, but they are not industrially
relevant. (89)
Rare earth! metals likewise are too difficult to produce and too reactive
to remain in the metallic state. Although widely found as oxide promoters
and supports, (90) there is no example of successful catalysis with rare earth
metals.