Page 65 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 65
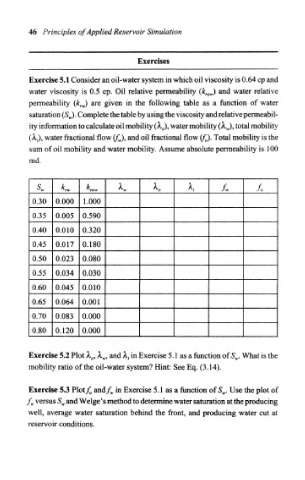
46 Principles of Applied Reservoir Simulation
Exercises
Exercise 5.1 Consider an oil-water system in which oil viscosity is 0.64 cp and
water viscosity is 0.5 cp. Oil relative permeability (k row) and water relative
permeability (Ar w) are given in the following table as a function of water
saturation (S w). Complete the table by using the viscosity and relative permeabil-
ity information to calculate oil mobility (A, 0), water mobility (A. w), total mobility
(1,), water fractional flow (/"„,), and oil fractional flow (£,). Total mobility is the
sum of oil mobility and water mobility. Assume absolute permeability is 100
md.
s w - *n. ^ row k *, L L
^
0.30 0.000 1.000
0.35 0.005 0.590
0.40 0.010 0.320
0.45 0.017 0.180
0.50 0.023 0.080
0.55 0.034 0.030
0.60 0.045 0.010
0.65 0.064 0.001
0.70 0.083 0.000
0.80 0.120 0.000
Exercise 5.2 Plot X 0, X w, and A, in Exercise 5.1 as a function of S w. What is the
mobility ratio of the oil-water system? Hint: See Eq. (3.14).
and/,, in Exercise 5.1 as a function of S w. Use the plot of
Exercise 5.3 Piotf 0
versus S w and Welge's method to determine water saturation at the producing
f w
well, average water saturation behind the front, and producing water cut at
reservoir conditions.