Page 175 - Principles of Catalyst Development
P. 175
CATALYST CHARACTERIZATfON 163
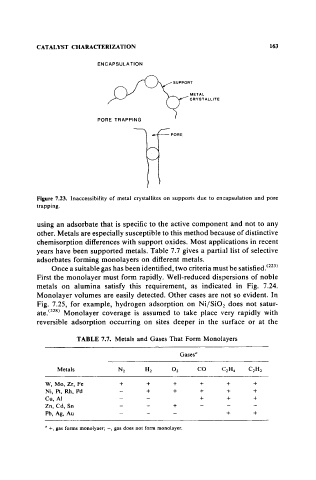
ENCAPSULA TlON
SUPPORT
METAL
CRVST AlllTE
PORE TRAPPING
PORE
Figure 7.23. Inaccessibility of metal crystallites on supports due to encapsulation and pore
trapping.
using an adsorbate that is specific to the active component and not to any
other. Metals are especially susceptible to this method because of distinctive
chemisorption differences with support oxides. Most applications in recent
years have been supported metals. Table 7.7 gives a partial list of selective
adsorbates forming monolayers on different metals.
Once a suitable gas has been identified, two criteria must be satisfied. (223)
First the monolayer must form rapidly. Well-reduced dispersions of noble
metals on alumina satisfy this requirement, as indicated in Fig. 7.24.
Monolayer volumes are easily detected. Other cases are not so evident. In
Fig. 7.25, for example, hydrogen adsorption on Ni/Si0 2 does not satur-
ate.(228) Monolayer coverage is assumed to take place very rapidly with
reversible adsorption occurring on sites deeper in the surface or at the
TABLE 7.7. Metals and Gases That Form Monolayers
Gases"
Metals N2 H2 O2 CO C2H 4 C2H2
W, Mo, Zr, Fe + + + + + +
Ni, Pt, Rh, Pd + + + + +
Cu, Al + + +
Zn, Cd, Sn +
Pb, Ag, Au + +
" +, gas forms monolyaer; -, gas does not form monolayer.