Page 191 -
P. 191
6.4 Region-Based Mining 173
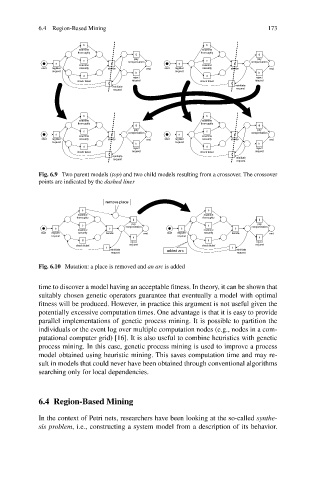
Fig. 6.9 Two parent models (top) and two child models resulting from a crossover. The crossover
points are indicated by the dashed lines
Fig. 6.10 Mutation: a place is removed and an arc is added
time to discover a model having an acceptable fitness. In theory, it can be shown that
suitably chosen genetic operators guarantee that eventually a model with optimal
fitness will be produced. However, in practice this argument is not useful given the
potentially excessive computation times. One advantage is that it is easy to provide
parallel implementations of genetic process mining. It is possible to partition the
individuals or the event log over multiple computation nodes (e.g., nodes in a com-
putational computer grid) [16]. It is also useful to combine heuristics with genetic
process mining. In this case, genetic process mining is used to improve a process
model obtained using heuristic mining. This saves computation time and may re-
sult in models that could never have been obtained through conventional algorithms
searching only for local dependencies.
6.4 Region-Based Mining
In the context of Petri nets, researchers have been looking at the so-called synthe-
sis problem, i.e., constructing a system model from a description of its behavior.