Page 106 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 106
Radionuclides in Nature 95
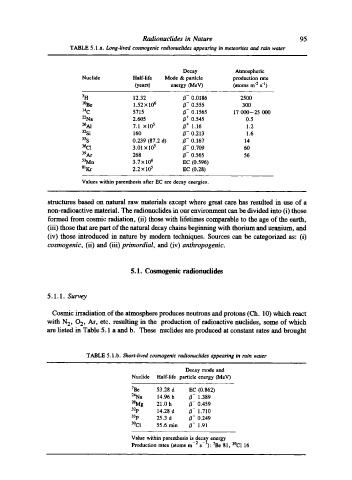
TABLE 5.1 .a. Long-lived cosmogenic radionuclides appearing in meteorites and rain water
Decay Atmospheric
Nuclide Half-life Mode & particle production rate
(years) energy (MeV) (atoms m "2 s q)
3H 12.32 B- 0.0186 2500
l~ 1.52 • 106 /~- 0.555 300
laC 5715 B- 0.1565 17 000-25 000
22Na 2.605 B + 0.545 0.5
26A1 7.1 x 105 B + 1.16 1.2
32Si 160 /~- 0.213 1.6
35S 0.239 (87.2 d) B- 0.167 14
3~C1 3.01 x 105 B- 0.709 60
39Ar 268 B- 0.565 56
53Mn 3.7 x 106 EC (0.596)
SlKr 2.2 x 105 EC (0.28)
Values within parenthesis after EC are decay energies.
structures based on natural raw materials except where great care has resulted in use of a
non-radioactive material. The radionuclides in our environment can be divided into (i) those
formed from cosmic radiation, (ii) those with lifetimes comparable to the age of the earth,
(iii) those that are part of the natural decay chains beginning with thorium and uranium, and
(iv) those introduced in nature by modem techniques. Sources can be categorized as: (i)
cosmogenic, (ii) and (iii)primordial, and (iv) anthropogenic.
5.1. Cosmogenic radionudides
5.1.1. Survey
Cosmic irradiation of the atmosphere produces neutrons and protons (Ch. 10) which react
with N 2, 0 2, Ar, etc. resulting in the production of radioactive nuclides, some of which
are listed in Table 5.1 a and b. These nuclides are produced at constant rates and brought
TABLE 5.1 .b. Short-lived cosmogenic radionuclides appearing in rain water
Decay mode and
Nuclide Half-life particle energy OVIeV)
7Be 53.28 d EC (0.862)
24Na 14.96 h B- 1.389
2SMg 21.0 h /~- 0.459
32p 14.28 d B- 1.710
33p 25.3 d /~- 0.249
39(71 55.6 min ~- 1.91
Value within parenthesis is decay energy
Production rates (atoms m-: s- l): 7Be 81, 39Cl 16