Page 139 - Radiochemistry and nuclear chemistry
P. 139
124 Radiochemistry and Nuclear Chemistry
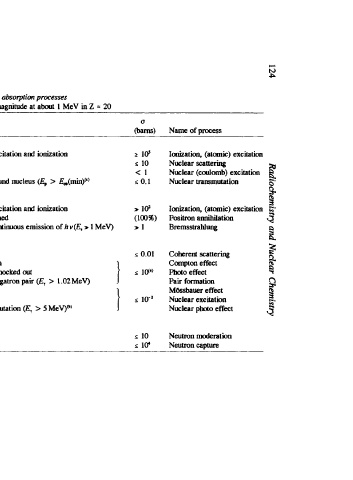
Name of process Ionization, (atomic) excitation Nuclear scattering Nuclear (coulomb) excitation Nuclear trammutation Ionization, (atomic) excitation Positron annihilation Bremsstrahlung scattering Coherent Compton effect photo effect Pair formation M6ssbauer effect Nuclear excitation Nuclear photo effect Neutron moderation Neutroncapture
(barn) lo' 10 0.1 (100%) 0.01 i 1W) 10-3
U 2 5 <I 5 > I@ >I 5 5 10 i l(r
= 20 MeV) 1
magnitude at about 1 MeV in 2 5 MeV)*) >
TABLE 6.1. Survey of nuclear radiation absorption pmesses
Type of reaction through atomic excitation and ionization Particle captured, formation of comparnd nucleus (E, > E&in)@) Particle energy loss through atomic excitation and ionization annihilated, 2-3 phdons formed Particle scattered with energy loss. continucus emission of h v(E, y scattered with energy loss, ionization y completely absorbed, one electron knocked out y annihilated, formation of positrownegatron pair (E, > 1.02 MeV) y absorbed by mleus, mlear transmutation (E,
reaction cross-sections (0) give only order of
Particle energy loss Particle elastically scattered Particle inelastically scattered Slow p' y scattered witholll energy loss y scattered without energy loss y scattered with ene%y loss n scattered with energy loss n captured. nuclear transformation strongly with decreasing energy. 1.6 MeV, D(y,n)H 2.2 MeV.
The react with is the Coulomb barrier energy, eqn. (12.18).
Reacting particles and fields Protovts Md heavier ions react with orbital electrons 4 atomic nucleus Electrons (e-, p-, pi) orbital electrons electric feld of nucleus (y) react with field of orbital electrons (outer) electrons bound (irmer) electrons Rlclear force atomic nucleus Neutrons react with atomic nucleus See Fig. 6.17; u increases Threshold energy for Ek(y,a)'He
Photons
field of
free
(') @) &(min) (')
1 la Id 2 2b 2c 3 3a 3b 3c 3d 4 4b