Page 359 - Reciprocating Compressors Operation Maintenance
P. 359
344 Reciprocating Compressors: Operation and Maintenance
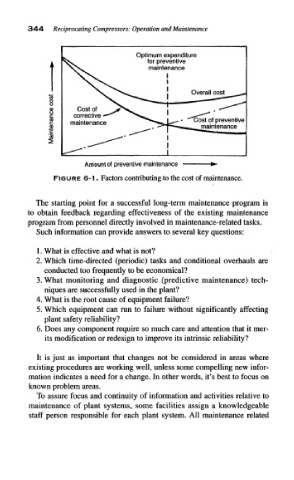
Optimum expenditure
for preventive
maintenance
v>
8
Cost of
corrective
maintenance Cost of preventive
maintenance
Amount of preventive maintenance
FIGURE 6-1. Factors contributing to the cost of maintenance.
The starting point for a successful long-term maintenance program is
to obtain feedback regarding effectiveness of the existing maintenance
program from personnel directly involved in maintenance-related tasks.
Such information can provide answers to several key questions:
1. What is effective and what is not?
2. Which time-directed (periodic) tasks and conditional overhauls are
conducted too frequently to be economical?
3. What monitoring and diagnostic (predictive maintenance) tech-
niques are successfully used in the plant?
4. What is the root cause of equipment failure?
5. Which equipment can run to failure without significantly affecting
plant safety reliability?
6. Does any component require so much care and attention that it mer-
its modification or redesign to improve its intrinsic reliability?
It is just as important that changes not be considered in areas where
existing procedures are working well, unless some compelling new infor-
mation indicates a need for a change. In other words, it's best to focus on
known problem areas.
To assure focus and continuity of information and activities relative to
maintenance of plant systems, some facilities assign a knowledgeable
staff person responsible for each plant system. All maintenance related