Page 87 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 87
62 Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
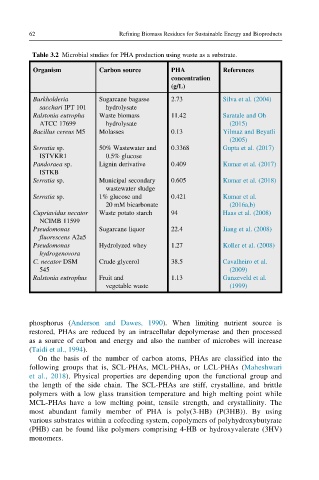
Table 3.2 Microbial studies for PHA production using waste as a substrate.
Organism Carbon source PHA References
concentration
(g/L)
Burkholderia Sugarcane bagasse 2.73 Silva et al. (2004)
sacchari IPT 101 hydrolysate
Ralstonia eutropha Waste biomass 11.42 Saratale and Oh
ATCC 17699 hydrolysate (2015)
Bacillus cereus M5 Molasses 0.13 Yilmaz and Beyatli
(2005)
Serratia sp. 50% Wastewater and 0.3368 Gupta et al. (2017)
ISTVKR1 0.5% glucose
Pandoraea sp. Lignin derivative 0.409 Kumar et al. (2017)
ISTKB
Serratia sp. Municipal secondary 0.605 Kumar et al. (2018)
wastewater sludge
Serratia sp. 1% glucose and 0.421 Kumar et al.
20 mM bicarbonate (2016a,b)
Cupriavidus necator Waste potato starch 94 Haas et al. (2008)
NCIMB 11599
Pseudomonas Sugarcane liquor 22.4 Jiang et al. (2008)
fluorescens A2a5
Pseudomonas Hydrolyzed whey 1.27 Koller et al. (2008)
hydrogenovora
C. necator DSM Crude glycerol 38.5 Cavalheiro et al.
545 (2009)
Ralstonia eutrophus Fruit and 1.13 Ganzeveld et al.
vegetable waste (1999)
phosphorus (Anderson and Dawes, 1990). When limiting nutrient source is
restored, PHAs are reduced by an intracellular depolymerase and then processed
as a source of carbon and energy and also the number of microbes will increase
(Taidi et al., 1994).
On the basis of the number of carbon atoms, PHAs are classified into the
following groups that is, SCL-PHAs, MCL-PHAs, or LCL-PHAs (Maheshwari
et al., 2018). Physical properties are depending upon the functional group and
the length of the side chain. The SCL-PHAs are stiff, crystalline, and brittle
polymers with a low glass transition temperature and high melting point while
MCL-PHAs have a low melting point, tensile strength, and crystallinity. The
most abundant family member of PHA is poly(3-HB) (P(3HB)). By using
various substrates within a cofeeding system, copolymers of polyhydroxybutyrate
(PHB) can be found like polymers comprising 4-HB or hydroxyvalerate (3HV)
monomers.