Page 90 - Refining Biomass Residues for Sustainable Energy and Bioproducts
P. 90
Microbial-derived natural bioproducts for a sustainable environment 65
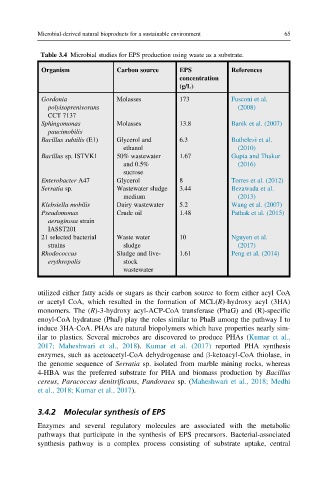
Table 3.4 Microbial studies for EPS production using waste as a substrate.
Organism Carbon source EPS References
concentration
(g/L)
Gordonia Molasses 173 Fusconi et al.
polyisoprenivorans (2008)
CCT 7137
Sphingomonas Molasses 13.8 Banik et al. (2007)
paucimobilis
Bacillus subtilis (E1) Glycerol and 6.3 Buthelezi et al.
ethanol (2010)
Bacillus sp. ISTVK1 50% wastewater 1.67 Gupta and Thakur
and 0.5% (2016)
sucrose
Enterobacter A47 Glycerol 8 Torres et al. (2012)
Serratia sp. Wastewater sludge 3.44 Bezawada et al.
medium (2013)
Klebsiella mobilis Dairy wastewater 5.2 Wang et al. (2007)
Pseudomonas Crude oil 1.48 Pathak et al. (2015)
aeruginosa strain
IASST201
21 selected bacterial Waste water 10 Nguyen et al.
strains sludge (2017)
Rhodococcus Sludge and live- 1.61 Peng et al. (2014)
erythropolis stock
wastewater
utilized either fatty acids or sugars as their carbon source to form either acyl CoA
or acetyl CoA, which resulted in the formation of MCL(R)-hydroxy acyl (3HA)
monomers. The (R)-3-hydroxy acyl-ACP-CoA transferase (PhaG) and (R)-specific
enoyl-CoA hydratase (PhaJ) play the roles similar to PhaB among the pathway I to
induce 3HA-CoA. PHAs are natural biopolymers which have properties nearly sim-
ilar to plastics. Several microbes are discovered to produce PHAs (Kumar et al.,
2017; Maheshwari et al., 2018). Kumar et al. (2017) reported PHA synthesis
enzymes, such as acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase and β-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, in
the genome sequence of Serratia sp. isolated from marble mining rocks, whereas
4-HBA was the preferred substrate for PHA and biomass production by Bacillus
cereus, Paracoccus denitrificans, Pandoraea sp. (Maheshwari et al., 2018; Medhi
et al., 2018; Kumar et al., 2017).
3.4.2 Molecular synthesis of EPS
Enzymes and several regulatory molecules are associated with the metabolic
pathways that participate in the synthesis of EPS precursors. Bacterial-associated
synthesis pathway is a complex process consisting of substrate uptake, central