Page 17 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 17
6 Reliability and Maintainability of In-Service Pipelines
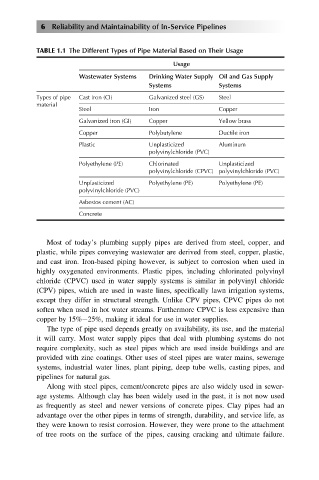
TABLE 1.1 The Different Types of Pipe Material Based on Their Usage
Usage
Wastewater Systems Drinking Water Supply Oil and Gas Supply
Systems Systems
Types of pipe Cast iron (CI) Galvanized steel (GS) Steel
material
Steel Iron Copper
Galvanized iron (GI) Copper Yellow brass
Copper Polybutylene Ductile iron
Plastic Unplasticized Aluminum
polyvinylchloride (PVC)
Polyethylene (PE) Chlorinated Unplasticized
polyvinylchloride (CPVC) polyvinylchloride (PVC)
Unplasticized Polyethylene (PE) Polyethylene (PE)
polyvinylchloride (PVC)
Asbestos cement (AC)
Concrete
Most of today’s plumbing supply pipes are derived from steel, copper, and
plastic, while pipes conveying wastewater are derived from steel, copper, plastic,
and cast iron. Iron-based piping however, is subject to corrosion when used in
highly oxygenated environments. Plastic pipes, including chlorinated polyvinyl
chloride (CPVC) used in water supply systems is similar in polyvinyl chloride
(CPV) pipes, which are used in waste lines, specifically lawn irrigation systems,
except they differ in structural strength. Unlike CPV pipes, CPVC pipes do not
soften when used in hot water streams. Furthermore CPVC is less expensive than
copper by 15% 25%, making it ideal for use in water supplies.
The type of pipe used depends greatly on availability, its use, and the material
it will carry. Most water supply pipes that deal with plumbing systems do not
require complexity, such as steel pipes which are used inside buildings and are
provided with zinc coatings. Other uses of steel pipes are water mains, sewerage
systems, industrial water lines, plant piping, deep tube wells, casting pipes, and
pipelines for natural gas.
Along with steel pipes, cement/concrete pipes are also widely used in sewer-
age systems. Although clay has been widely used in the past, it is not now used
as frequently as steel and newer versions of concrete pipes. Clay pipes had an
advantage over the other pipes in terms of strength, durability, and service life, as
they were known to resist corrosion. However, they were prone to the attachment
of tree roots on the surface of the pipes, causing cracking and ultimate failure.