Page 82 - Reliability and Maintainability of In service Pipelines
P. 82
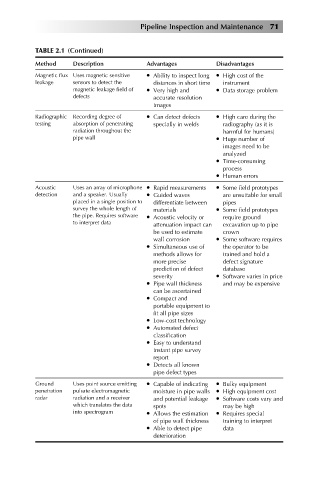
Pipeline Inspection and Maintenance 71
TABLE 2.1 (Continued)
Method Description Advantages Disadvantages
Magnetic flux Uses magnetic sensitive Ability to inspect long High cost of the
leakage sensors to detect the distances in short time instrument
magnetic leakage field of Very high and Data storage problem
defects accurate resolution
images
Radiographic Recording degree of Can detect defects High care during the
testing absorption of penetrating specially in welds radiography (as it is
radiation throughout the harmful for humans)
pipe wall Huge number of
images need to be
analyzed
Time-consuming
process
Human errors
Acoustic Uses an array of microphone Rapid measurements Some field prototypes
detection and a speaker. Usually Guided waves are unsuitable for small
placed in a single position to differentiate between pipes
survey the whole length of materials Some field prototypes
the pipe. Requires software Acoustic velocity or require ground
to interpret data attenuation impact can excavation up to pipe
be used to estimate crown
wall corrosion Some software requires
Simultaneous use of the operator to be
methods allows for trained and hold a
more precise defect signature
prediction of defect database
severity Software varies in price
Pipe wall thickness and may be expensive
can be ascertained
Compact and
portable equipment to
fit all pipe sizes
Low-cost technology
Automated defect
classification
Easy to understand
instant pipe survey
report
Detects all known
pipe defect types
Ground Uses point source emitting Capable of indicating Bulky equipment
penetration pulsate electromagnetic moisture in pipe walls High equipment cost
radar radiation and a receiver and potential leakage Software costs vary and
which translates the data spots may be high
into spectrogram Allows the estimation Requires special
of pipe wall thickness training to interpret
Able to detect pipe data
deterioration