Page 222 - Reservoir Geomechanics
P. 222
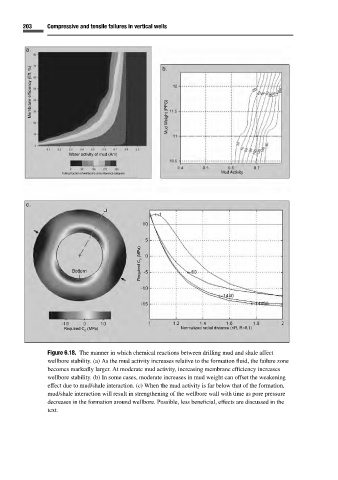
203 Compressive and tensile failures in vertical wells
a. b.
Membrane efficiency (Eff, %) Mud Weight (PPG)
Water activity of mud (Am)
Failing fraction of wellbore’s circumference (degree) Mud Activity
c.
Required C 0 (MPa)
Required C (MPa) Normalized radial distance (r/R, R=0.1)
0
Figure 6.18. The manner in which chemical reactions between drilling mud and shale affect
wellbore stability. (a) As the mud activity increases relative to the formation fluid, the failure zone
becomes markedly larger. At moderate mud activity, increasing membrane efficiency increases
wellbore stability. (b) In some cases, moderate increases in mud weight can offset the weakening
effect due to mud/shale interaction. (c) When the mud activity is far below that of the formation,
mud/shale interaction will result in strengthening of the wellbore wall with time as pore pressure
decreases in the formation around wellbore. Possible, less beneficial, effects are discussed in the
text.