Page 216 - Robot Builder's Bonanza
P. 216
UNDERSTANDING BATTERY RATINGS 185
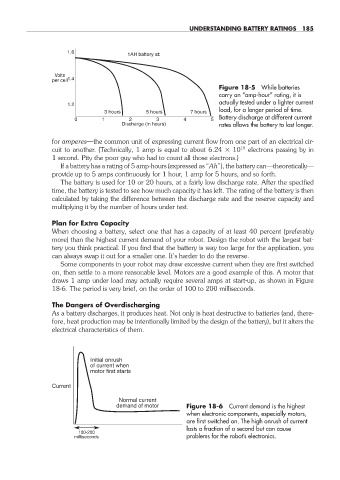
1.6
1AH battery at:
Volts
per cell 1.4
Figure 18- 5 While batteries
carry an “amp- hour” rating, it is
actually tested under a lighter current
1.2
load, for a longer period of time.
3 hours 5 hours 7 hours
0 1 2 3 4 5 Battery discharge at different current
Discharge (in hours) rates allows the battery to last longer.
for amperes— the common unit of expressing current flow from one part of an electrical cir-
18
cuit to another. (Technically, 1 amp is equal to about 6.24 10 electrons passing by in
1 second. Pity the poor guy who had to count all those electrons.)
If a battery has a rating of 5 amp- hours (expressed as “Ah”), the battery can— theoretically—
provide up to 5 amps continuously for 1 hour, 1 amp for 5 hours, and so forth.
The battery is used for 10 or 20 hours, at a fairly low discharge rate. After the specified
time, the battery is tested to see how much capacity it has left. The rating of the battery is then
calculated by taking the difference between the discharge rate and the reserve capacity and
multiplying it by the number of hours under test.
Plan for Extra Capacity
When choosing a battery, select one that has a capacity of at least 40 percent (preferably
more) than the highest current demand of your robot. Design the robot with the largest bat-
tery you think practical. If you find that the battery is way too large for the application, you
can always swap it out for a smaller one. It’s harder to do the reverse.
Some components in your robot may draw excessive current when they are first switched
on, then settle to a more reasonable level. Motors are a good example of this. A motor that
draws 1 amp under load may actually require several amps at start- up, as shown in Figure
18- 6. The period is very brief, on the order of 100 to 200 milliseconds.
The Dangers of Overdischarging
As a battery discharges, it produces heat. Not only is heat destructive to batteries (and, there-
fore, heat production may be intentionally limited by the design of the battery), but it alters the
electrical characteristics of them.
Initial onrush
of current when
motor first starts
Current
Normal current
demand of motor Figure 18- 6 Current demand is the highest
when electronic components, especially motors,
are first switched on. The high onrush of current
lasts a fraction of a second but can cause
100-200
milliseconds problems for the robot’s electronics.
18-chapter-18.indd 185 4/21/11 11:49 AM