Page 181 - Robotics Designing the Mechanisms for Automated Machinery
P. 181
4.7 Electrically Controlled Vibration Dampers 169
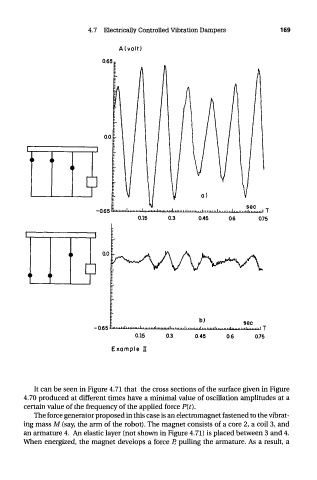
It can be seen in Figure 4.71 that the cross sections of the surface given in Figure
4.70 produced at different times have a minimal value of oscillation amplitudes at a
certain value of the frequency of the applied force P(t).
The force generator proposed in this case is an electromagnet fastened to the vibrat-
ing mass M (say, the arm of the robot). The magnet consists of a core 2, a coil 3, and
an armature 4. An elastic layer (not shown in Figure 4.71) is placed between 3 and 4.
When energized, the magnet develops a force P, pulling the armature. As a result, a