Page 223 - Robots Androids and Animatrons : 12 Incredible Projects You Can Build
P. 223
Radio
Link
Camera
Eyes Robot
Display
Human
Slave
Movement Master
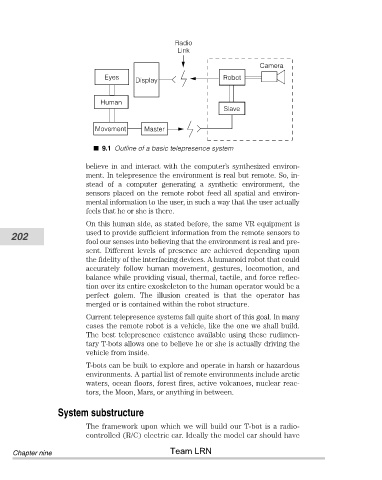
9.1 Outline of a basic telepresence system
believe in and interact with the computer’s synthesized environ-
ment. In telepresence the environment is real but remote. So, in-
stead of a computer generating a synthetic environment, the
sensors placed on the remote robot feed all spatial and environ-
mental information to the user, in such a way that the user actually
feels that he or she is there.
On this human side, as stated before, the same VR equipment is
used to provide sufficient information from the remote sensors to
202
fool our senses into believing that the environment is real and pre-
sent. Different levels of presence are achieved depending upon
the fidelity of the interfacing devices. A humanoid robot that could
accurately follow human movement, gestures, locomotion, and
balance while providing visual, thermal, tactile, and force reflec-
tion over its entire exoskeleton to the human operator would be a
perfect golem. The illusion created is that the operator has
merged or is contained within the robot structure.
Current telepresence systems fall quite short of this goal. In many
cases the remote robot is a vehicle, like the one we shall build.
The best telepresence existence available using these rudimen-
tary T-bots allows one to believe he or she is actually driving the
vehicle from inside.
T-bots can be built to explore and operate in harsh or hazardous
environments. A partial list of remote environments include arctic
waters, ocean floors, forest fires, active volcanoes, nuclear reac-
tors, the Moon, Mars, or anything in between.
System substructure
The framework upon which we will build our T-bot is a radio-
controlled (R/C) electric car. Ideally the model car should have
Team LRN
Chapter nine