Page 394 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 394
PILLAR SUPPORTED MINING METHODS
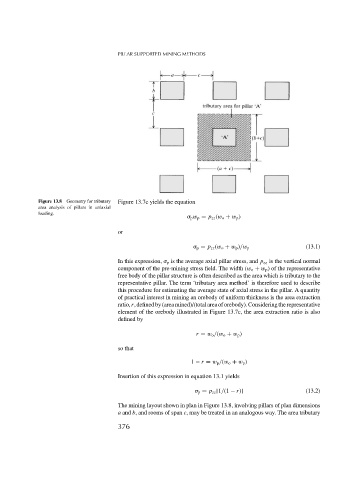
Figure 13.8 Geometry for tributary Figure 13.7c yields the equation
area analysis of pillars in uniaxial
loading.
p w p = p zz (w o + w p )
or
(13.1)
p = p zz (w o + w p )/w p
In this expression, p is the average axial pillar stress, and p zz is the vertical normal
component of the pre-mining stress field. The width (w o + w p ) of the representative
free body of the pillar structure is often described as the area which is tributary to the
representative pillar. The term ‘tributary area method’ is therefore used to describe
this procedure for estimating the average state of axial stress in the pillar. A quantity
of practical interest in mining an orebody of uniform thickness is the area extraction
ratio,r,definedby(areamined)/(totalareaoforebody).Consideringtherepresentative
element of the orebody illustrated in Figure 13.7c, the area extraction ratio is also
defined by
r = w o /(w o + w p )
so that
1 − r = w p /(w o + w p )
Insertion of this expression in equation 13.1 yields
p = p zz [1/(1 − r)] (13.2)
The mining layout shown in plan in Figure 13.8, involving pillars of plan dimensions
a and b, and rooms of span c, may be treated in an analogous way. The area tributary
376