Page 491 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 491
BLOCK CAVING
abutment stress concentration. When stresses are high, this may be sufficient to cause
distress to the extraction level installations.
The advantages of pre-undercutting are that the extraction level is developed in a
de-stressed environment, the undercut can be mined independently of the extraction
level, support and reinforcement requirements on the extraction level are generally
lower than for the post-undercutting method, and the broken ore in the undercut level
acts as rock fill reducing the abutment loads on the undercut face to some extent.
The disadvantages of this strategy include the need for a separate ore handling
facility on the undercut level, possible sequencing problems between extraction hori-
zon development and undercutting, the need to develop drawbells from the extraction
level into broken rock on the undercut level, possible high stress remnants arising
from the compaction of blasted undercut ore making extraction horizon develop-
ment difficult, drawpoint hang-ups resulting from ore compaction, and slower initial
production arising from these various factors.
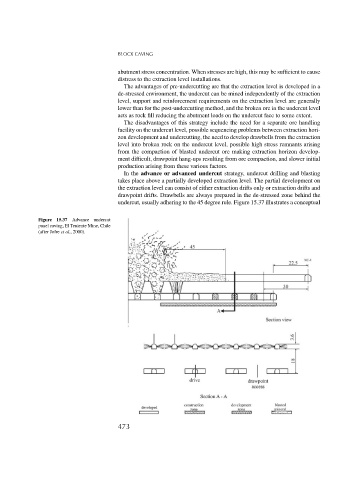
In the advance or advanced undercut strategy, undercut drilling and blasting
takes place above a partially developed extraction level. The partial development on
the extraction level can consist of either extraction drifts only or extraction drifts and
drawpoint drifts. Drawbells are always prepared in the de-stressed zone behind the
undercut, usually adhering to the 45 degree rule. Figure 15.37 illustrates a conceptual
Figure 15.37 Advance undercut
panel caving, El Teniente Mine, Chile
(after Jofre et al., 2000).
473