Page 517 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 517
DISCONTINUOUS SUBSIDENCE ASSOCIATED WITH CAVING METHODS OF MINING
SURFACE TERRAIN D D
SURFACE TERRAIN
C C
A A
S S
CRATER WALL
CRATER WALL
t i t i
z z
BROKEN MATERIAL
BROKEN MATERIAL
H H t t
C C
h h
α α β β
DRIFT AFFECTED BY SUBSIDENCE
DRIFT AFFECTED BY SUBSIDENCE
A B
A B
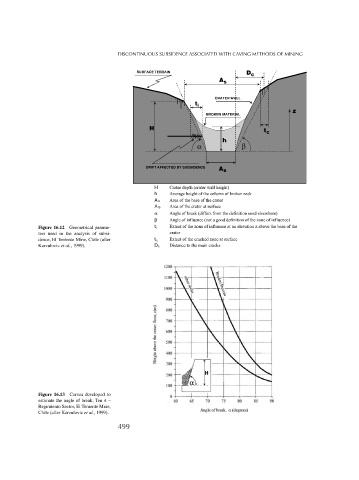
H Crater depth (crater wall height)
h Average height of the column of broken rock
A b Area of the base of the crater
A S Area of the crater at surface
α Angle of break (differs from the definition used elsewhere)
β Angle of influence (not a good definition of the zone of influence)
Figure 16.12 Geometrical parame- t i Extent of the zone of influence at an elevation z above the base of the
ters used in the analysis of subsi- crater
dence, El Teniente Mine, Chile (after t c Extent of the cracked zone at surface
Karzulovic et al., 1999). Dc Distance to the main cracks
Figure 16.13 Curves developed to
estimate the angle of break, Ten 4 –
Regimiento Sector, El Teniente Mine,
Chile (after Karzulovic et al., 1999).
499